Carbapenem Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Cases from India: An Overview of Current Knowledge
Abstract:
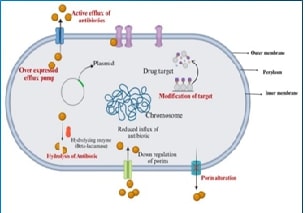
Carbapenem-resistant
Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) is a significant public health concern in India.
Our current review attempts a qualitative summary of observational studies
published in the last ten years. The key resistance mechanisms identified
include carbapenemase enzymes like New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM-1),
Oxacillinase-48 (OXA-48), and Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC), as
well as non-enzymatic factors such as efflux pump overexpression and
alterations in outer membrane porins (OmpK35, OmpK36). Horizontal gene transfer
via plasmids and transposons was also observed to accelerate the dissemination
of resistance genes. Carbapenem resistance rates in India have surged from 9%
in 2008 to approximately 60% by 2024. Environmental contamination from
untreated industrial and hospital waste, along with antibiotic overuse, also
significantly contributed to the increased spread of CRKp strains and is
associated with mortality rates of around 68%. Challenges in the diagnosis of
CRKp cases arise from limitations of phenotypic methods and the non-availability
of genotypic techniques such as PCR and whole-genome sequencing in
resource-constrained settings. Treatment options against CRKp are limited,
often relying on last-resort antibiotics like polymyxins and tigecycline, which
also have significant side effects and face rising resistance. Emerging
therapies, including novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations and
agents like cefiderocol, show a promising option but require further
validation. Therefore, an urgent, integrated approach is recommended to combat rising
CRKp infections in India, which involves enhancing surveillance systems,
strengthening antimicrobial stewardship programs, improving infection control
practices within healthcare facilities, and promoting public education on the
risks of antibiotic misuse.
References:
[1]. Ahmadi,
Z., Noormohammadi, Z., Behzadi, P., & Ranjbar, R., 2022, Molecular
detection of gyra mutation in clinical strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Iranian Journal of Public Health,
51(10), 2334–2339.
[2]. Shamanna,
V., Srinivas, S., Couto, N., Nagaraj, G., Sajankila, S. P., Krishnappa, H. G.,
Kumar, K. A., Aanensen, D. M., & Lingegowda, R. K., 2024, Geographical
distribution, disease association and diversity of klebsiella pneumoniae k/l
and o antigens in india: roadmap for vaccine development. Microbial
genomics, 10(7).
[3]. Indrajith,
S., Mukhopadhyay, A. K., Chowdhury, G., Farraj, D. A. A., Alkufeidy, R. M.,
Natesan, S., Meghanathan, V., Gopal, S., &Muthupandian, S., 2020, Molecular
insights of carbapenem resistance Klebsiella
pneumoniae isolates with focus on multidrug resistance from clinical
samples. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 14(1), 131–138.
[4]. Shankar, C., Nabarro, l. E., Anandan, S., et al., 2018, Extremely
high mortality rates in patients with carbapenem-resistant, hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae blood stream
infections. The journal of the association of physicians of india,
66(12), 13–16.
[5]. Das,
B. J., Banerjee, T., Wangkheimayum, J., et al., 2024, Characterization of
blaoxa-232 carrying carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella
pneumoniae (crkp) & their expression profiles under selective
carbapenem pressure: an in-depth study from India. The Indian Journal of
Medical Research, 159(6), 644–652.
[6]. Verma, G., Nayak, S. R., Jena, S., Panda, S. S., Pattnaik, D., Praharaj,
A., & Singh, N., 2023, Prevalence of carbapenem-resistant
enterobacterales, Acinetobacter baumannii,
and pseudomonas aeruginosa in a tertiary care hospital in eastern India: a
pilot study. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 17(4), 2243–2249.
[7]. Veeraraghavan, B., Shankar, C., Karunasree, S., Kumari, S., Ravi, R.,
& Ralph, R., 2017, Carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from bloodstream infection: indian
experience. Pathogens and Global Health, 111(5), 240–246.
[8]. Kunjalwar,
R., &Mudey, G., 2024, A cross-sectional study on endemicity of vim, ndm,
kpc, ipm& oxa-48 genes in carbapenemase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia
coli from a tertiary hospital using mcim, ecim, and pcr in central india.
F1000research, 13, 636.
[9]. Mohanty,
S., Mittal, G., &Gaind, R., 2017, Identification of carbapenemase-mediated
resistance among enterobacteriaceae bloodstream isolates: a molecular study
from India. Indian journal of medical microbiology, 35(3), 421–425.
[10]. Firoozeh,
F., Mahluji, Z., Shams, E., Khorshidi, A., &Zibaei, M., 2017, New
delhimetallo-β-lactamase-1-producing klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in
hospitalized patients in kashan, iran. Iranian Journal of Microbiology, 9(5),
283–287.
[11]. Mulvey,
M. R., Grant, J. M., Plewes, K., Roscoe, D., &Boyd, D. A., 2011, New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase
in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli, Canada. Emerging
infectious diseases, 17(1), 103–106.
[12]. Gupta, V., Garg, R., Kumaraswamy, K., et al., 2018, Phenotypic
and genotypic characterization of carbapenem resistance mechanisms in Klebsiella pneumoniae from blood culture
specimens: a study from north India. Journal of Laboratory Physicians,
10(02), 125-129.
[13]. Nachimuthu, R., Subramani, R., Maray, S., Gothandam, K. M., Sivamangala,
K., Manohar, P., & Bozdogan, B., 2016, Characterization
of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria from Tamil Nadu. Journal of
chemotherapy, 28(5), 371–374.
[14]. Tsai,
Y., Fung, C., Lin, J., Chen, J., Chang, F., Chen, T., & Siu, l. K., 2011, Klebsiella pneumoniae outer membrane
porins ompk35 and ompk36 play roles in both antimicrobial resistance and
virulence. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 55(4), 1485–1493.
[15]. Kong,
H., Pan, Q., Lo, W., Liu, X., Law, C. O. K., Chan, T., Ho, P., &Lau, T. C.,
2018, Fine-tuning carbapenem resistance by reducing porin permeability of
bacteria activated in the selection process of conjugation. Scientific
reports, 8(1).
[16]. Gupta, A. K., Chauhan, D. S., Srivastava, K., Das, R., Batra, S., &
Mittal, M., 2010, Estimation of efflux-mediated multi-drug resistance
and its correlation with expression levels of two major efflux pumps in
mycobacteria. Journal of communicable diseases, 38(3), 246-254.
[17]. Garima,
K., Pathak, R., Tandon, R., Rathor, N., Sinha, R., &Bose, M., 2015,
Differential expression of efflux pump genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in response to varied subinhibitory
concentrations of anti-tuberculosis agents. Tuberculosis (edinburgh), 95(2),
155-161.
[18]. Narang, A., Garima, K., Porwal, S., Bhandekar, A., Shrivastava, K.,
Giri, A., Sharma, N. K., Bose, M., & Varma-basil, M., 2019b, Potential
impact of efflux pump genes in mediating rifampicin resistance in clinical
isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
from India. Plos one, 14(9), e0223163.
[19]. Bhatia,
M., Shamanna, V., Nagaraj, G., Sravani, D., Gupta, P., Omar, B. J.,
Chakraborty, D., &Ravikumar, K. L., 2021, Molecular characterisation of
carbapenem-resistantklebsiellapneumoniaeclinical isolates: preliminary
experience from a tertiary care teaching hospital in the himalayas. Transactions
of the royal society of tropical medicine and hygiene, 116(7), 655–662.
[20]. Tayyaba,
U., Khan, S. W., Sultan, A., Khan, F., Akhtar, A., Nagaraj, G., Ahmed, A.,
&Bhattacharya, B., 2024, Molecular characterization of mdr and xdr clinical
strains from a tertiary care center in North India by whole genome sequence
analysis. Journal of the Oman Medical Association, 1(1), 29–47.
[21]. Shukla,
S., Desai, S., Bagchi, A., Singh, P., Joshi, .M, Joshi, C., Patankar, J.,
maheshwari, P., Rajni, E., Shah, M., &Gajjar, d., 2023, Diversity and
distribution of β-lactamase genes circulating in indian isolates of
multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Antibiotics, 12(3), 449.
[22]. Spadar, A., Phelan, J., Elias, R., Modesto, A., Caneiras,
C., Marques, C., Lito, l., Pinto, M., Cavaco-silva, P., Ferreira, H., Pomba,
C., Da silva, G. J., aSavedra, M. J., Melo-cristino, J., Duarte, A., Campino,
S., Perdigão, J., &Clark, T. G., 2022, Genomic epidemiological analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae from portuguese
hospitals reveals insights into circulating antimicrobial resistance. Scientific
reports, 12(1).
[23]. Li, P., Luo, W., Xiang, T., Jiang, Y., Liu, P., Wei, D., Fan, l., Huang,
S., Liao, W., Liu, Y., & Zhang, W., 2022, Horizontal gene
transfer via omvs co-carrying virulence and antimicrobial-resistant genes is a
novel way for the dissemination of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Frontiers in
microbiology, 13. Https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.945972
[24]. Apisarnthanarak, A., Hsu, l. Y., Khawcharoenporn, T., & Mundy, l.
M., 2013, Carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria: how to
prioritize infection prevention and control interventions in resource-limited
settings. Expert review of anti-infective therapy, 11(2), 147-157.
[25]. Muresu, N., Deiana, G., Dettori, M., Palmieri, A.,
Masia, M. D., Cossu, A., . &Castiglia, p., 2023, Infection
prevention control strategies of new delhimetallo-β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. In healthcare (vol. 11, no. 18, p. 2592). Mdpi.
[26]. Anagnostopoulos,
D. A., Parlapani, F. F., Natoudi, S., Syropoulou, F., Kyritsi, M., Vergos, I.,
Hadjichristodoulou, C., Kagalou, I., &Boziaris, I. S., 2022, Bacterial
communities and antibiotic resistance of potential pathogens involved in food
safety and public health in fish and water of lake karla, thessaly, greece. Pathogens, 11(12), 1473.
[27]. Sivalingam, P. J., Poté, & Prabakar, K., 2019, Environmental
prevalence of carbapenem resistance enterobacteriaceae (cre) in a tropical
ecosystem in India: human health perspectives and future directives. Pathogens,
8(4), 174.
[28]. Sree,
R. A., Gupta, A., Gupta, N., Veturi, S., Reddy, L. S. K., Begum, M., Shravani,
E., Challa, H. R., Reddy, S. S., Singamsetty, A., Arumilli, M., Reddy, P. N.,
& Tirlangi, P. K., 2024, Ceftazidime-avibactam alone or in combination with
Aztreonam versus Polymyxins in the management of carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial
Infections (CAPRI study): a retrospective cohort study from South India. Infection, 52(2),
429–437.
[29]. Kim,
H. K., Park, J. S., Sung, H., &Kim, M. N., 2015, Further modification of
the modified hodge test for detecting metallo-β-lactamase-producing
carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae. Annals of laboratory medicine,
35(3), 298.
[30]. Hamal, D., Shrestha, R., Paudel, R., Nayak, N., Bhatta, D. R., &
Gokhale, s., 2023, Combined disc test and modified hodge test for
detection of carbapenemase-producing gram-negative bacilli. Nepal journal of
medical sciences, 8(2), 15-21.
[31]. Wang,
Y., Huang, X., Yin, D., Shen, S., Jian, C., Sun, Z., &Chen, Z, 2024,
Modification of carbapenemase inhibition test and comparison of its performance
with ng-test carba 5 for detection of carbapenemase-producing enterobacterales.
Journal of applied microbiology, lxae197.
[32]. Kibwana,
U. O., Manyahi, J., Moyo, S. J., Blomberg, B., Roberts, A. P., Langeland, N.,
&Mshana, S. E., 2024, Antimicrobial resistance profile of enterococcus
species and molecular characterization of vancomycin resistant enterococcus
faecium from the fecal samples of newly diagnosed adult hiv patients in dar es
salaam, tanzania. Frontiers in tropical diseases, 5, 1307379.
[33]. Christina,
S., Praveena, R., Shahul, M. R., &Saikumar, c., 2024,
Carbapenemase-producing escherichia coli: comparison of a novel rapid lateral
flow assay with the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) and antimicrobial
resistance pattern. Cureus, 16(9), e68941.
[34]. Way,
Y. A., Huang, C. W., Liao, W. C., Li, S. W., Chiang, R. L., Hsing, E. W.,
&Hsieh, y. C., 2024, Sequential use of capsular typing and whole-genome
sequencing-based analysis for transmission of carbapenem-resistant
acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary medical center. Journal of
microbiology, immunology and infection.
[35]. Naik,
V. V., Kumar, S., Thrimurthy, T., Channareddy, V., &Shaw, T., 2024,
Enhancing carbapenem resistance detection: lamp coupled with melting curve
analysis-for rapid molecular diagnostics in clinical specimens.
[36]. Tempe,
D. K., Agarwal, J., Chaudhary, K., Lalwani, P., Tudu, M. S., Hansdah, U.,
&Mishra, B., 2015, Carbapenem resistance patterns in general intensive care
unit of a tertiary care hospital in india. Mamc journal of medical sciences,
1(2), 85-91.
[37]. Veeraraghavan, B., Shankar, C., Karunasree, S., Kumari, S., Ravi, R.,
& Ralph, R., 2017, Carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from bloodstream infection: indian
experience. Pathogens and global health, 111(5), 240-246.
[38]. Way,
Y. A., Huang, C. W., Liao, W. C., Li, S. W., Chiang, R. L., Hsing, E. W.,
&Hsieh, y. C., 2024, Sequential use of capsular typing and whole-genome
sequencing-based analysis for transmission of carbapenem-resistant
acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary medical center. Journal of
microbiology, immunology and infection.
[39]. Vieceli,
T., Henrique, l. R., Rech, T. H., & Zavascki, A. P., 2024, Colistin versus
polymyxin b for the treatment of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae
bloodstream infections. Journal of infection and chemotherapy, 30(7),
621-625.
[40]. Tiseo,
G., Galfo, V., Riccardi, N., Suardi, l. R., Pogliaghi, M., Giordano, C.,
&Falcone, m., 2024, Real-world experience with meropenem/vaborbactam for
the treatment of infections caused by esbl-producing enterobacterales and
carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.
European journal of clinical microbiology & infectious diseases,
1-8.
[41]. Sophonsri, A., Kalu, M., & Wong-beringer, A., 2024, Comparative
in vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam, imipenem-relebactam, and
meropenem-vaborbactam against carbapenem-resistant clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics,
13(5), 416.
[42]. Yang,
C., Wang, l., Lv, J., Wen, Y., Gao, Q., Qian, F., & Du, H., 2024, Effects
of different carbapenemase and siderophore production on cefiderocol
susceptibility in Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, e01019-24.
[43]. Mantzarlis,
K., Manoulakas, E., Parisi, K., Sdroulia, E., Zapaniotis, N., Tsolaki, V.,
&Makris, D., 2024, Meropenem plus ertapenem and ceftazidime–avibactam plus
aztreonam for the treatment of ventilator associated pneumonia caused by
pan-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics, 13(2), 141.
[44]. Zhong,
W., Fu, Y., Liao, X., Xu, N., Shen, l., Wu, J., & Yang, C., 2024, Enhancing
safe and effective treatment of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with polymyxin b-loaded dendritic
nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 498, 155753.
[45]. Kou, X., Yang, X., & Zheng, R., 2024, Challenges and
opportunities of phage therapy for klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Applied
and environmental microbiology, e01353-24.
[46]. Zhou, H., Du, X., Wang, Y., Kong, J., Zhang, X.,
Wang, W., . & Ye, J., 2024, Antimicrobial peptide a20l: in
vitro and in vivo antibacterial and antibiofilm activity against
carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Microbiology spectrum, 12(8), e03979-23.
[47]. Zhu,
J., Chen, T., Ju, Y., Dai, J., &Zhuge, X., 2024, Transmission dynamics and
novel treatments of high risk carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: the lens of one health. Pharmaceuticals,
17(9), 1206.
[48]. Fritzenwanker,
M., Imirzalioglu, C., Herold, S., Wagenlehner, F. M., Zimmer, K. P.,
&Chakraborty, T., 2018, Treatment options for carbapenem- resistant
gram-negative infections. Deutschesarzteblatt international, 115(20-21),
345–352.
[49]. Kontopidou,
F., Giamarellou, H., Katerelos, P., Maragos, A., Kioumis, I., Trikka-graphakos,
E., Valakis, C., &Maltezou, H., 2013, Infections caused by
carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
among patients in intensive care units in greece: a multi-centre study on
clinical outcome and therapeutic options. Clinical microbiology and
infection, 20(2), o117–o123.
[50]. Tesfa,
T., Mitiku, H., Edae, M., &Assefa, N., 2022, Prevalence and incidence of
carbapenem-resistant K.pneumoniae
colonization: systematic review and meta-analysis. Systematic reviews,
11(1), 240.
[51]. Ramasubramanian,
V., Porwal, R., &Rajesh, N., 2014, Carbapenem resistant gram-negative
bacteremia in an indian intensive care unit: a review of the clinical profile
and treatment outcome of 50 patients. Indian journal of critical care
medicine, 18(11), 750–753.
[52]. Suay-García,
B., &Pérez-gracia, M. T., 2021, Present and future of carbapenem-resistant
enterobacteriaceae infections. Advances in clinical immunology, medical
microbiology, COVID-19, and big data, 435-456.
[53]. Mascellino,
M. T., Oliva, A., Biswas, S., & Ceccarelli, G., 2024, Editorial: New
therapeutic strategies against carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative
bacteria. Frontiers in microbiology,15, 1513900. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1513900
[54]. Swaminathan,
S., Routray, A., & Mane, A., 2022, Early and appropriate use of
ceftazidime-avibactam in the management of multidrug-resistant gram-negative
bacterial infections in the indian scenario. Cureus, 14(8), e28283.
[55]. Muresu, N., Deiana, G., Dettori, M., Palmieri, A.,
Masia, M. D., Cossu, A., &Castiglia, P., 2023, Infection
prevention control strategies of new delhimetallo-β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. In healthcare
(vol. 11, no. 18, p. 2592). Mdpi.
[56]. Amit,
S., Mishali, H., Kotlovsky, T., Schwaber, M. J., &Carmeli, Y., 2014,
Bloodstream infections among carriers of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella
pneumoniae: etiology, incidence and predictors. Clinical microbiology and
infection, 21(1), 30–34.
[57]. Kaur, J. N., Singh, N., Smith, N. M., Klem, J. F.,
Cha, R., Lang, Y., . &Tsuji, B. T., 2024, Next-generation
antibiotic combinations to combat pan-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Scientific reports, 14(1), 3148.
[58]. Hu, F., Pan, Y., Li, H., Han, H., Liu, X., Ma, R., &
He, P., 2024, Carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae capsular types,
antibiotic resistance and virulence factors in China: a longitudinal,
multi-centre study. Nature microbiology, 9(3), 814-829.
[59]. Ph, S., Attavar, P. C., Tr, R., Kotian, M. S., & Ns, D., 2024, Emergence
of high-level antibiotic resistance in Klebsiella
pneumoniae: a narrative review. South asian journal of research in
microbiology, 18(2), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.9734/sajrm/2024/v18i2343

