Association of Cardiometabolic Diseases in Adolescents with Level of Obesity and Lifestyle Pattern at Metropolitan City; Findings from Southern India
Abstract:
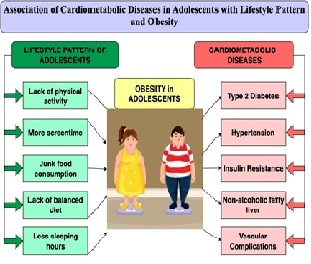
The crisis of obesity is observed among adolescents in metropolitan
cities in India. It is associated with a range of cardiometabolic diseases,
such as hypertension, prediabetes, Asthma, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidaemia,
and reproductive abnormalities. The objective of this study was to analyse the
cardiometabolic risk factors and weight status of adolescents in association
with their lifestyle patterns. A cross-sectional study was conducted among
adolescent patients who received treatment for cardiometabolic disease in a tertiary
care hospital. They were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. 83
adolescent patients with obesity were identified and interviewed. General
information, lifestyle patterns and details of the cardiometabolic risk factors
were collected through a questionnaire. ANOVA was calculated using SPSS Version
23, and the statistically significant level was <0.05. There was an
association between age group, family income, physical activity, screen time, junk
food consumption, balanced diet and sleeping hours in obesity-level adolescent
patients. The mean values of cardiometabolic diseases were worse in obesity III
and II than in obesity I. The status of blood pressure (SBP and DBP), fasting
PG, total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglyceride strongly correlated with
adolescent patients' level of obesity. Lifestyle modifications are essential
among adolescents to prevent comorbidities that have developed from
cardiometabolic risk factors.
References:
[1].
Yang, L., Magnussen, C. G., Yang, L., Bovet, P., Xi, B.,
2020, Elevated Blood Pressure in Childhood
or Adolescence and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Adulthood: A Systematic Review. Hypertension, 75:948–55.
[2]. Lessard, L. M., Lawrence, S. E., 2022,
Weight-Based Disparities in Youth Mental Health: Scope, Social Underpinnings,
and Policy Implications. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain
Sciences, 9(1):49-56, https://doi.org/10.1177/23727322211068018.
[3]. WHO, 2024, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
[4]. Navarro, P., Shivappa, N., Hébert, J. R., Mehegan, J., Murrin,
C. M., Kelleher, C. C., et al., 2020, Predictors of
the dietary inflammatory index in children and associations with childhood
weight status. Clin Nutr, 39:2169–79, https://10.1016/j.clnu.2019.09.004.
[5].
Suganya,
M., Kalabarathi, S., 2024, Association of body mass index with dietary intake
and self-care health activities of mothers after postpartum: A mixed-method
research in Chennai City, India. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis, 14:52–7, https://doi.org/10.4103/ijnpnd.ijnpnd_71_23.
[6]. Maria Aashitha, Harsavarthini, K. R.,
Subashchandra, K., 2024, A cross-sectional study on Dietary Health Risk
Behaviours and Hygiene Practices among Adolescent Students in Urban Chennai,
Tamil Nadu. African Journal of Biological Sciences, 6(Si4):1805-10,
ISSN: 2663-2187, https://doi.org/10.48047/AFJBS.6.Si4.2024.1804-1810.
[7]. Suganya,
M., Kalabarathi, S., 2024, Efficacious Maintenance-Electroconvulsive Therapy
(m-ECT) and Antipsychotic Medication for Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder in a
Young Adult Woman in Chennai, India: A Case Report. International Journal of
Nutrition, Pharmacology, Neurological Diseases, 14(3):390-392, https://doi.org/10.4103/ijnpnd.ijnpnd_42_24.
[8]. Hendryx, M., Chojenta, C., Byles, J.
E., 2020, Obesity
Risk Among Young Australian Women: A Prospective Latent Class Analysis, Obesity (Silver Spring, Md), 28:154–60, https://10.1002/oby.22646.
[9].
Suganya, M., Padmapriya, D., 2024, Determinants and
levels of depression among young adult patients with epilepsy: a
cross-sectional study in a Tertiary Care Hospital, Tamilnadu, India, International
Journal of Nutrition, Pharmacology, Neurological Diseases, 14(4): 432-436, https://doi.org/10.4103/ijnpnd.ijnpnd_112_24.
[10].
Qin, T. T., Xiong, H. G., Yan, M. M., Sun, T., Qian, L., Yin,
P., 2019, Body
weight misperception and weight disorders among Chinese children and
adolescents: a latent class analysis, Curr Med Sci, 39:852–62,
https://10.1007/s11596-019-2116-1.
[11].
Suganya, M., Maragatham, S., Sheela, P., 2024, Assessment
on Health Status of Adult Patients with Osteoarthritis of the Lower Limb by
Western Ontario and McMaster’s Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC): A Study
in Chennai City, Texila International Journal of Public Health, Special
Issue:1-8, https://doi.org/10.21522/TIJPH.2013.SE.24.02.art007.
[13].
Al-Mhanna, S. B., Rocha-Rodriguesc, S., Mohamed, M.,
Batrakoulis, A., Aldhahi, M. I., Afolabi, H. A., Yagin, F. H., Alhussain, M. H.,
Gulu, M., Abubakar, B. D., Ghazali, W. S. W., Alghannam, A. F., Badicu, G.,
2023, Effects of combined aerobic exercise and diet on cardiometabolic health
in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil, Dec 4;15(1):165, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13102-023-00766-5.
[14]. Lim, S. Y., Chan, Y. M.,
Chin, Y. S., Zalilah, M. S., Ramachandran, V., Arumugam, M., 2024, Combined
Effect of Dietary Acid Load and Cardiometabolic Syndrome on Bone Resorption
Marker among Post-Menopausal Women in Malaysia. Malays J Med Sci, 31(2):113-129,
https://doi.org/10.21315/mjms2024.

