Tuberculosis Treatment as the First Priority Indicator of Public Health in the Healthy Indonesia Program with a Family Approach
Abstract:
Public health care is part of the "Healthy
Indonesia Program with a Family Approach", which consists of 5 indicators,
namely treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis sufferers according to standards,
regular treatment of hypertension sufferers, treatment and not neglecting
sufferers of mental disorders, absence of family members who smoke, and family
membership in national health insurance. This study aimed to select maternal
and child health indicators based on priority using the difficulty-usefulness
pyramid (DUP). The respondents of this study were 329 families in Indonesia
selected using the snowball sampling technique. The difficulty and usefulness
of the five indicators were measured using an online questionnaire, then
analyzed and presented in the form of a difficulty-usefulness pyramid. The
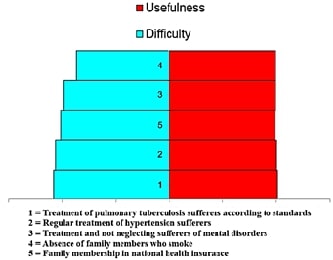
results of the analysis showed that the range based on the total
difficulty-usefulness for each indicator was 1) treatment of pulmonary
tuberculosis sufferers according to standards = 17.21; 2) regular treatment of
hypertension sufferers = 17.00; 3) treatment and not neglecting sufferers of
mental disorders = 16.53; 4) absence of family members who smoke = 16.37; and
5) family membership in national health insurance = 15.46. After the range was
sorted, the largest range was at the base of the pyramid. It could be concluded
that the indicator of public health care that was prioritized was the treatment
of pulmonary tuberculosis sufferers according to standards.
References:
[1].
Maryani, H., Rizkianti, A., Izza, N., 2024,
Classification of healthy family indicators in indonesia based on a K-means
cluster analysis. J Prev Med Public Health, 57(3), 234-241.
[2].
Hardjito, K., Rahmaningtyas, I., Nugroho, H. S. W.,
2023, Selection of prioritized healthy family indicators, using the
difficulty-usefulness pyramid (DUP). Rawal Medical Journal, 48(1),
168-172.
[3].
Bisri, M., Handoko, R., Darmawan, A., 2023, Implementation
of the healthy indonesia program with a family approach (PIS-PK) at community
health centers in Bintan District, Kepulauan Riau Province. International
Journal of Social Science, 2(6), 2423-2428.
[4].
Saloner, B., Wilk, A. S., Levin, J., 2020, Community health
centers and access to care among underserved populations: A synthesis review. Med
Care Res Rev, 77(1), 3-18.
[5].
Trisna, N., 2021, Implementation of a healthy
indonesian programs with a family approach (PIS-PK) (Study at Puskesmas Seluma
Timur). International Journal of Policy and Public Administration, 2(1),
26-36.
[6].
Nugroho, H. S. W., Sillehu. S., Handoyo, Suparji,
Sunarto, Subagyo, Sunarko, B., Bahtiar, 2018, Difficultness-Usefulness Pyramid
(DUP) as new method to select elements prioritized in management of e-learning
in health. Indian Journal of Public Health Research and Development,
9(2), 206-211.
[7].
Nugroho, H. S. W., Handoyo, Prayitno, H., Budiono, A.,
2019, Sort elements based on priority, in order to improve the quality of
e-learning in health using Difficulty-Usefulness Pyramid with Weighting
(DUP-We). International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET),
14(18), 186-193.
[8].
Ibrahim, I., Sudiana. I. K., Mukono, H. J., Suhartono,
Nugroho, H. S. W., 2020, Determination of priority elements of vigilance in the
use of pesticides based on difficulty and usefulness (A supporting study for
law and policy in health). Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine and
Toxicology, 14(2), 1615-1619.
[9].
Ibrahim, I., Sudiana, I. K., Mukono, H. J., Suhartono,
Nugroho, H. S. W., 2020, Awareness program of pesticides used among farmers
using Difficulty-Usefulness Pyramid (A suggestion for health laws and policies
regarding the use of pesticides). Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine and
Toxicology, 14(3), 1946-1951.
[10]. Nugroho,
H. S. W., Suparji, S., Sunarto, S., Handoyo, H., Yessimbekov, Z., Burhanuddin,
N., Selasa, P., 2020, Quadrant of Difficulty-Usefulness (QoDU) as new method in
preparing for improvement of e-learning in health college. Risk Manag
Healthc Policy, 13, 1625-1632.
[11].
Sunarto,
S., Nugroho, H. S. W., Suparji, S., Santosa, B. J., 2024, Quadrant of
difficulty and usefulness for prioritizing community-based disaster
preparedness parameter elements. RMJ, 49(1):172-175.
[12]. Main, S.,
Lestari. T., Triasih, R., Chan, G., Davidson, L., Majumdar, S., Santoso, D.,
Phung, S., Laukkala, J., Graham, S., du Cros, P., Ralph, A., 2019, Training for
tuberculosis elimination in Indonesia: Achievements, reflections, and potential
for impact. Trop Med Infect Dis., 4(3), 107.
[13]. Ritonga,
I. L., Setyowati, S., Handiyani, H., Nursasi, A. Y., 2023, Exploring the
tuberculosis medication program in Indonesia as perceived by patients and their
families: A qualitative study. Belitung Nurs J., 9(2), 124-131.
[14]. Lestari, T.,
Fuady, A., Yani, F. F., Putra. I. W. G. A. E., Pradipta, I. S., Chaidir, L.,
Handayani, D., Fitriangga, A., Loprang, M. R., Pambudi, I., Ruslami, R.,
Probandari, A., 2023, The development of the national tuberculosis research
priority in Indonesia: A comprehensive mixed-method approach. PLoS One,
18(2), e0281591.
[15]. Oktamianti,
P., Bachtiar, A., Sutoto, S., Trihandini, I., Prasetyo, S., Achadi, A., Efendi,
F., 2021, Tuberculosis control within Indonesia's hospital accreditation. J
Public Health Res., 10(3), 1979.
[16]. Winardi,
W., Wahyuni, H., Hidayat, M., Wirawan, A., Nurwidya, F., Uddin, M. N., Yusup,
M., 2022, Challenges on tuberculosis care in health care facilities during
COVID-19 pandemic: Indonesian perspective. Narra J., 2(2), e80.
[17]. Iskandar,
D., Suwantika, A. A., Pradipta, I. S., Postma, M. J., van Boven, J. F. M.,
2023, Clinical and economic burden of drug-susceptible tuberculosis in
Indonesia: national trends 2017-2019. Lancet Glob Health, 11(1),
e117-e125.
[18]. Fahdhienie,
F., Mudatsir, M., Abidin, T. F., Nurjannah, N., 2024, Risk factors of pulmonary
tuberculosis in Indonesia: A case-control study in a high disease prevalence
region. Narra J., 4(2), e943.
[19]. Dana, N. R.,
Rika, S., M, I. P., Alexander, M. B., Muthia, S., Linda, R., Astri, W., Zuhrah,
T., Rahman, A. D., Rahmi, F., Nomira, P., Setia, N. D. A. W., Arif, L. B. L.,
Ainil. M., Octarini, E. M., Nova, L., Tamia, M. Y., Sri, R. A., Permata, S. A.,
Mimin, O., Puspa, H. F., Fariz, A. M., 2024, Modifiable and non-modifiable risk
factors for tuberculosis among adults in indonesia: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Afr J Infect Dis., 18(2), 19-28.
[20]. Kaaffah, S.,
Kusuma, I. Y., Renaldi, F. S., Lestari, Y. E., Pratiwi, A. D. E., Bahar, M. A.,
2023, Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of tuberculosis in Indonesia: A multi-center
cross-sectional study. Infect Drug Resist., 16, 1787-1800.
[21]. Main, S.,
Triasih, R., Greig, J., Hidayat, A., Brilliandi, I. B., Khodijah, S., Chan, G.,
Wilks, N., Parry, A. E., Nababan, B., du Cros, P., Dwihardiani, B., 2023, The
prevalence and risk factors for tuberculosis among healthcare workers in
Yogyakarta, Indonesia. PLoS One, 18(5), e0279215.
[22]. Soeroto, A.
Y., Pratiwi, C., Santoso, P., Lestari, B. W., 2021, Factors affecting outcome
of longer regimen multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment in West Java
Indonesia: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE, 16(2), e0246284.
[23]. Juliasih,
N. N., Mertaniasih, N. M., Hadi, C., Soedarsono, Sari, R. M., Alfian, I. N.,
2020, Factors affecting tuberculosis patients' quality of life in Surabaya,
Indonesia. J Multidiscip Healthc., 13, 1475-1480.

