Camptothecin Anti-cancer Activity Against Breast Cancer Cells (MDA MB-231) Targeting the Gene Expression of Wnt/Beta-catenin Pathway - An In silico and In vitro Approach
Abstract:
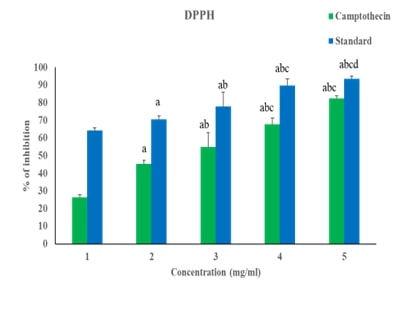
Camptothecin, a potent anti-cancer agent, exhibits significant activity against MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by targeting the gene expression of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. This pathway is crucial in cancer progression and cell proliferation. Camptothecin's effect on this pathway is elucidated through various assays and docking techniques. The DPPH assay demonstrates camptothecin's antioxidant potential, indicating its ability to neutralize free radicals. Additionally, nitric oxide assays reveal a significant enhancement in antioxidant properties, further supporting its therapeutic potential. Gene expression analysis provides insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying camptothecin's anti-cancer effects. The expression levels of key components of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, including Wnt, β-catenin, APC, GSK3β, LP5, and Axin, are significantly altered in MDA-MB-231 cells upon camptothecin treatment. These changes suggest a disruption in the signaling pathway, which is vital for cancer cell survival and proliferation. The MTT assay results highlight camptothecin's capacity to inhibit cell growth in a time-dependent manner, underscoring its efficacy in reducing cancer cell viability over prolonged exposure. Moreover, docking studies indicate a high binding affinity between camptothecin and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway components, reinforcing the compound's role in modulating this critical signaling axis. Overall, camptothecin's multi-faceted approach, encompassing antioxidant activity and targeted gene expression modulation, presents a compelling case for its use in breast cancer therapy. The comprehensive analysis of its effects on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway offers valuable insights into its mechanism of action and potential as a therapeutic agent against aggressive breast cancer types like MDA-MB-231 cells.References:
[1].
Venditto,
V. J., & Simanek, E. E., 2010, Cancer therapies utilizing the
camptothecins: a review of the in vivo literature. Molecular Pharmaceutics,
7(2), 307–349. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp900243b
[2].
Narasimhan,
A., Sampath, S., Jayaraman, S., & Karundevi, B., 2013, Estradiol favors
glucose oxidation in gastrocnemius muscle through modulation of insulin
signaling molecules in adult female rats. Endocrine Research, 38(4),
251-262.
[3].
Roy,
J. R., Janaki, C. S., Jayaraman, S., Periyasamy, V., Balaji, T., Vijayamalathi,
M., & Veeraraghavan, V. P., 2022, Effect of Carica papaya on IRS-1/Akt
signaling mechanisms in high-fat-diet-streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic
experimental rats: A mechanistic approach. Nutrients, 14(19), 4181.
[4].
Perumal,
S., Langeshwaran, K., Selvaraj, J., Ponnulakshmi, R., Shyamaladevi, B., &
Balasubramanian, M. P., 2018, Effect of diosmin on apoptotic signaling
molecules in N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in
experimental rats. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 449, 27-37.
[5].
Devarajan,
N., Jayaraman, S., Mahendra, J., Venkatratnam, P., Rajagopal, P., Palaniappan,
H., & Ganesan, S. K., 2021, Berberine—A potent chemosensitizer and
chemoprotector to conventional cancer therapies. Phytotherapy Research,
35(6), 3059-3077.
[6].
Jayaraman,
S., Natararaj, S., & Veeraraghavan, V. P., 2024, Hesperidin inhibits oral
cancer cell growth via apoptosis and inflammatory signaling-mediated
mechanisms: Evidence from in vitro and in silico analyses. Cureus,
16(2).
[7].
Jayaraman,
S., Natarajan, S. R., Veeraraghavan, V. P., & Jasmine, S., 2023, Unveiling
the anti-cancer mechanisms of calotropin: Insights into cell growth inhibition,
cell cycle arrest, and metabolic regulation in human oral squamous carcinoma
cells (HSC-3). Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research, 13(6),
704-713.
[8].
Jayaraman,
S., Veeraraghavan, V. P., Natarajan, S. R., & Jasmine, S., 2024, Exploring
the therapeutic potential of curcumin in oral squamous cell carcinoma (HSC-3
cells): Molecular insights into hypoxia-mediated angiogenesis. Pathology-Research
and Practice, 254, 155130.
[9].
Jayaraman,
S., Natarajan, S. R., Ponnusamy, B., Veeraraghavan, V. P., & Jasmine, S., 2023,
Unlocking the potential of beta sitosterol: Augmenting the suppression of oral
cancer cells through extrinsic and intrinsic signalling mechanisms. The
Saudi Dental Journal, 35(8), 1007-1013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sdentj.2023.08.003
[10].
Roy,
J. R., Janaki, C. S., Jayaraman, S., Periyasamy, V., Balaji, T., Vijayamalathi,
M., & Veeraraghavan, V. P., 2022, Carica papaya reduces muscle insulin
resistance via IR/GLUT4 mediated signaling mechanisms in high fat diet and
streptozotocin-induced type-2 diabetic rats. Antioxidants, 11(10), 2081.
[11].
Roy,
J. R., Janaki, C. S., Jayaraman, S., Periyasamy, V., Balaji, T., Vijayamalathi,
M., & Prasad, M., 2023, Carica papaya reduces high fat diet and
streptozotocin-induced development of inflammation in adipocyte via
IL-1β/IL-6/TNF-α mediated signaling mechanisms in type-2 diabetic rats. Current
Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(2), 852.
[12].
Baliyan,
S., Mukherjee, R., Priyadarshini, A., Vibhuti, A., Gupta, A., Pandey, R. P.,
& Chang, C. M., 2022, Determination of Antioxidants by DPPH Radical
Scavenging Activity and Quantitative Phytochemical Analysis of Ficus religiosa.
Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 27(4), 1326. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041326
[13].
Chen,
K., Pittman, R. N., & Popel, A. S., 2008, Nitric oxide in the vasculature:
where does it come from and where does it go? A quantitative perspective. Antioxidants
& Redox Signaling, 10(7), 1185–1198. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2007.1959
[14].
Krishnamoorthy,
K., Natarajan, S. R., Veeraraghavan, V. P., & Jayaraman, S., 2024,
Blueberry extract and its bioactive compounds mitigate oxidative stress and
suppress human lung cancer cell (A549) growth by modulating the expression of
p53/EGFR/STAT3/IL6-mediated signaling molecules. Cell Biochemistry and
Function, 42(4), e4027. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.4027
[15].
Indu,
S., Vijayalakshmi, P., Selvaraj, J., & Rajalakshmi, M., 2021, Novel
triterpenoids from Cassia fistula stem bark depreciates STZ-induced detrimental
changes in IRS-1/Akt-mediated insulin signaling mechanisms in type-1 diabetic
rats. Molecules, 26(22), 6812.
[16].
Deenadayalan,
A., Subramanian, V., Paramasivan, V., Veeraraghavan, V. P., Rengasamy, G.,
Coiambatore Sadagopan, J., & Jayaraman, S., 2021, Stevioside attenuates
insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by facilitating IR/IRS-1/Akt/GLUT 4
signaling pathways: An in vivo and in silico approach. Molecules,
26(24), 7689.
[17].
Chang,
L. C., Chen, T. C., Chen, S. J., Chen, C. L., Lee, C. C., Wu, S. H., & Lin,
J. J., 2016, Identification of a new class of WNT1 inhibitor: Cancer cells
migration, G-quadruplex stabilization and target validation. Oncotarget,
7(42), 67986.
[18].
Khademian,
N., Mirzaei, A., Hosseini, A., Zare, L., Nazem, S., Babaheidarian, P., &
Tavakoli-Yaraki, M., 2022, Expression pattern and clinical significance of
β-catenin gene and protein in patients with primary malignant and benign bone
tumors. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 9488.
[19].
Domoto,
T., Uehara, M., Bolidong, D., & Minamoto, T., 2020, Glycogen synthase
kinase 3β in cancer biology and treatment. Cells, 9(6), 1388.
[20].
Prasad, M., Gatasheh, M. K.,
Alshuniaber, M. A., Krishnamoorthy, R., Rajagopal, P., Krishnamoorthy, K., et
al. 2022, Impact of Glyphosate on the Development of Insulin Resistance in
Experimental Diabetic Rats: Role of NFκB Signalling Pathways. Antioxidants
(Basel), 11(12), 2436. http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122436
[21].
Vishaka, S., Sridevi, G., Selvaraj,
J., 2022, An in vitro analysis on the antioxidant and anti-diabetic properties
of Kaempferia galanga rhizome using different solvent systems. J Adv Pharm
Technol Res, 13(Suppl 2), S505–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/japtr.japtr_189_22
[22].
Chandran, D., Jayaraman, S.,
Sankaran, K., Veeraraghavan, V. P., Gayathri, R., 2023, Antioxidant Vitamins
Attenuate Glyphosate-Induced Development of Type-2 Diabetes Through the
Activation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 β and Forkhead Box Protein O-1 in the
Liver of Adult Male Rats. Cureus, 15(12), e51088. doi:
10.7759/cureus.51088.
[23].
El-Sayed,
A. S. A., Hassan, W. H. B., Sweilam, S. H., Alqarni, M. H. S., El Sayed, Z. I.,
Abdel-Aal, M. M., Abdelsalam, E., & Abdelaziz, S., 2022, Production,
Bioprocessing and Anti-Proliferative Activity of Camptothecin from Penicillium
chrysogenum, "An Endozoic of Marine Sponge, Cliona sp.", as a
Metabolically Stable Camptothecin Producing Isolate. Molecules (Basel,
Switzerland), 27(9), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27093033.
[24].
Yadalam,
P. K., Arumuganainar, D., Ronsivalle, V., Di Blasio, M., Badnjevic, A.,
Marrapodi, M. M., Cervino, G., & Minervini, G., 2024, Prediction of
interactomic hub genes in PBMC cells in type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia,
and periodontitis. BMC oral health, 24(1), 385. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-024-04041-y.
[25].
Al-Shorman,
H. M., Abu-Naba'a, L. A., Sghaireen, M. G., & Alam, M. K., 2024, The Effect
of Various Preparation and Cementation Techniques of Dental Veneers on
Periodontal Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. European Journal
of Dentistry, 18(2), 458–467. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1776120.
[26].
Mathew,
M. G., Jeevanandan, G., Vishwanathaiah, S., Hamzi, K. A., Depsh, M. A. N.,
& Maganur, P. C., 2022, Parental and Child Outlook on the Impact of ECC on
Oral Health-related Quality of Life: A Prospective Interventional Study. The
Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, 23(9), 877–882. https://doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3397
[27].
Jamshidi-Adegani,
F., Ghaemi, S., Al-Hashmi, S., Vakilian, S., Al-Kindi, J., Rehman, N. U., Alam,
K., Al-Riyami, K., Csuk, R., Arefian, E., & Al-Harrasi, A., 2022,
Comparative study of the cytotoxicity, apoptotic, and epigenetic effects of
Boswellic acid derivatives on breast cancer. Scientific Reports, 12(1),
19979. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24229-y
[28].
Hemmati
Bushehri, R., Navabi, P., Saeedifar, A. M., Keshavarzian, N., Hosseini
Rouzbahani, N., Mosayebi, G., Ghazavi, A., Ghorban, K., & Ganji, A., 2023,
Integration of phytotherapy and chemotherapy: Recent advances in anticancer
molecular pathways. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 26(9),
987–1000. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2023.69979.15222.
[29].
Lopes,
C. M., Dourado, A., & Oliveira, R., 2017, Phytotherapy and Nutritional
Supplements on Breast Cancer. BioMed Research International, 2017,
7207983. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7207983.
[30].
Bailly,
C., & Vergoten, G., 2023, Interaction of Camptothecin Anticancer Drugs with
Ribosomal Proteins L15 and L11: A Molecular Docking Study. Molecules (Basel,
Switzerland), 28(4), 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041828.
[31].
Wintola,
O. A., & Afolayan, A. J., 2011, Phytochemical constituents and antioxidant
activities of the whole leaf extract of Aloe ferox Mill. Pharmacognosy
Magazine, 7(28), 325–333. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1296.90414.
[32].
Simu,
S., Marcovici, I., Dobrescu, A., Malita, D., Dehelean, C. A., Coricovac, D.,
Olaru, F., Draghici, G. A., & Navolan, D., 2021, Insights into the Behavior
of Triple-Negative MDA-MB-231 Breast Carcinoma Cells Following the Treatment
with 17β-Ethinylestradiol and Levonorgestrel. Molecules (Basel,
Switzerland), 26(9), 2776. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092776.
[33].
Márquez-Garbán,
D. C., Yanes, C. D., Llarena, G., Elashoff, D., Hamilton, N., Hardy, M.,
Wadehra, M., McCloskey, S. A., & Pietras, R. J., 2024, Manuka Honey
Inhibits Human Breast Cancer Progression in Preclinical Models. Nutrients,
16(14), 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142369

