Evaluating the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Solvent Extracts from Gymnema Sylvestre Against Wound Pathogens
Abstract:
The antibacterial activity of Gymnema sylvestre solvent extracts,
including acetone, aqueous, chloroform, ethanol, and hydroxyethanol, is
assessed in this study against common wound infections. G. sylvestre is a
well-known traditional medicinal herb with a wide range of therapeutic uses
that has drawn attention due to its antibacterial actions. The release of
bioactive chemicals was optimized by the use of a systematic extraction process
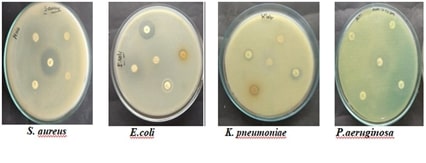
with several solvents. Using the agar well diffusion method, the antibacterial
activity of the extract was evaluated against a variety of wound
pathogens, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus. The findings showed that the
antibacterial activity of the various solvent extracts varied significantly.
The extracts of ethanol, acetone, chloroform, and hydroxyethanol showed the
strongest inhibitory effects, dramatically slowing the growth of the pathogens
under examination. Moderate action was demonstrated by aqueous extracts against
the acquired infections. These results indicate that the bioavailability of
antimicrobial compounds in G. sylvestre is significantly influenced by the
extraction solvent. The study emphasizes the potential of G.
sylvestre as a natural antibacterial agent, especially about wound
healing. The precise bioactive components causing this activity must be
determined, and their mechanisms of action must be investigated, through more
research. Overall, this research adds to the increasing evidence that supports
the use of herbal remedies for managing wound-related infections, providing
valuable insights for future therapeutic applications.
References:
[1].
Salam, M. A., Al-Amin,
M. Y., Salam, M. T., Pawar, J. S., Akhter, N., Rabaan, A. A., Alqumber, M. A.,
2023, Antimicrobial resistance: a growing serious threat for global public
health. In Healthcare 11(13), 1946.
[2]. Chiș, A. A., Rus, L. L., Morgovan, C., Arseniu, A.
M., Frum, A., Vonica-Țincu, A. L., Dobrea, C. M., 2022, Microbial resistance to
antibiotics and effective antibiotherapy. Biomedicines, 10(5),
1121.
[3]. Liu, G. Y., Yu, D., Fan, M. M., Zhang, X., Jin, Z.
Y., Tang, C., & Liu, X. F., 2024, Antimicrobial resistance crisis: could
artificial intelligence be the solution? Military Medical Research, 11(1),
7.
[4]. Patel, K., Patel, D. K., 2017, Medicinal
importance, pharmacological activities, and analytical aspects of hispidulin: A
concise report. Journal of traditional and complementary medicine, 7(3),
360-366.
[5]. Fatima, N., Baqri, S. S. R., Alsulimani, A.,
Fagoonee, S., Slama, P., Kesari, K. K., Haque, S., 2021, Phytochemicals from
Indian ethnomedicines: Promising prospects for the management of oxidative
stress and cancer. Antioxidants, 10(10), 1606.
[6].
Chaughule, R. S., Barve,
R. S., 2024, Role of herbal medicines in the treatment of infectious
diseases. Vegetos, 37(1), 41-51.
[7]. Courric, E., Brinvilier, D., Couderc, P.,
Ponce-Mora, A., Méril-Mamert, V., Sylvestre, M., Cebrian-Torrejon, G., 2023,
Medicinal plants and plant-based remedies in Grande-Terre: an
ethnopharmacological approach. Plants, 12(3), 654.
[8].
Vaou, N., Stavropoulou,
E., Voidarou, C., Tsigalou, C., & Bezirtzoglou, E., 2021, Towards advances
in medicinal plant antimicrobial activity: A review study on challenges and
future perspectives. Microorganisms, 9(10), 2041.
[9]. Ashraf, M. V., Pant, S., Khan, M. H., Shah, A. A.,
Siddiqui, S., Jeridi, M., Ahmad, S., 2023, Phytochemicals as antimicrobials:
prospecting Himalayan medicinal plants as source of alternate medicine to
combat antimicrobial resistance. Pharmaceuticals, 16(6), 881.
[10]. Entooru, K., Krishnaprasad, M. S., Thimmaiah, S.
B., Nanjaiah, S. K., Kolgi, R. R., Bopaiah, R. U., Thimmappa, N., 2021,
Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of leaf extract of Gymnema
sylvestre. IJCS, 9(2), 1123-1125.
[11]. Ramadass, N., Subramanian, N., Ponnulakshmi, R.,
Selvaraj, J., 2019, Phytochemical Screening and Antibacterial Activity of Leaf
Extracts of Gymnema sylvestre against Pathogenic Bacteria. Int. J. Sci.
Res. in Biological Sciences Vol, 6, 1.
[12]. Kavipriya, R., Ramasubburayan, R., 2024,
Phytofabrication of biocompatible zinc oxide nanoparticle using Gymnema
sylvestre and its potent in vitro antibacterial, antibiofilm, and cytotoxicity
against human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231). Bioprocess and
Biosystems Engineering, 1-15.
[13]. Arunachalam, K. D., Arun, L. B., Annamalai, S. K.,
Arunachalam, A. M., 2015, Potential anticancer properties of bioactive
compounds of Gymnema sylvestre and its biofunctionalized silver
nanoparticles. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 31-41.
[14]. Subramanian, S., Dowlath, M. J. H., Karuppannan,
S. K., Saravanan, M., Arunachalam, K. D., 2020. Effect of solvent on the
phytochemical extraction and GC-MS analysis of Gymnema sylvestre. Pharmacognosy
Journal, 12(4).
[15]. Kabeerdass, N.,
Thangasamy, S., Murugesan, K., Arumugam, N., Almansour, A. I., Suresh Kumar,
R., Mathanmohun, M., 2022, Embedding green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles
in cotton fabrics and assessment of their antibacterial wound healing and
cytotoxic properties: An eco-friendly approach. Green Processing and
Synthesis, 11(1), 875-885.
[16]. Kabeerdass, N., Kandasamy, S., Albasher, G.,
Alamri, O., Alsultan, N., Thangaswamy, S., Mathanmohun, M., 2022, Limonia
acidissima leaf mediated gold nanoparticles synthesis and their antimicrobial
and wound healing properties. Materials Letters, 314, 131893.
[17]. Muteeb, G., Rehman, M. T., Shahwan, M., &
Aatif, M., 2023, Origin of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance, and their
impacts on drug development: A narrative review. Pharmaceuticals, 16(11),
1615.
[18]. Chaachouay, N., Zidane, L., 2024, Plant-derived
natural products: a source for drug discovery and development. Drugs
and Drug Candidates, 3(1), 184-207.
[19]. Arora, D. S., Sood, H., 2017, In vitro
antimicrobial potential of extracts and phytoconstituents from Gymnema
sylvestre R. Br. leaves and their biosafety evaluation. AMB express, 7,
1-13.
[20]. Xu, Z., Li, M., Li, Y., Cao, H., Miao, L., Xu, Z.,
Yan, A., 2019, Native CRISPR-Cas-mediated genome editing enables dissecting and
sensitizing clinical multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. Cell Reports, 29(6),
1707-1717.
[21]. Hafiz, T. A., Alanazi, S., Alghamdi, S. S.,
Mubaraki, M. A., Aljabr, W., Madkhali, N., Alotaibi, F., 2023, Klebsiella
pneumoniae bacteraemia epidemiology: resistance profiles and clinical outcome
of King Fahad Medical City isolates, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. BMC Infectious
Diseases, 23(1), 579.
[22]. Linz, M. S., Mattappallil, A., Finkel, D., Parker,
D. 2023, Clinical impact of Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft tissue
infections. Antibiotics, 12(3), 557.
[23]. Zhou, Y., Zhou, Z., Zheng, L., Gong, Z., Li, Y.,
Jin, Y., Chi, M., 2023, Urinary tract infections caused by uropathogenic
Escherichia coli: mechanisms of infection and treatment options. International
journal of molecular sciences, 24(13), 10537.
[24]. Gunasekaran, V., Srinivasan, S., Rani, S., 2019,
Potential antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Gymnema sylvestre related
to diabetes. J. Med. Plants, 7(2), 05-11.
[25]. Solanki, P., Arora, A., 2024, Isolation and
characterization of peptides from Gymnema sylvestre and their antimicrobial
assay against bacterial isolates of diabetic foot ulcer. Journal of
Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 13(4), 154-160.
[26]. Ganesan, M., Muthaiah,
C., Wadaan, M. A., Kumar, M., Yanto, D. H. Y., Kumar, S., Suganthi, S., 2024,
Synthesis and characterization of fluorinated graphene oxide nanosheets derived
from Lissachatina fulica snail mucus and their biomedical applications. Luminescence, 39(9),
e4875.
[27]. Saritha, P.,
Arunprakash, S., Srinivasan, P., Selvankumar, T., Aldawood, S., Kim, W., Song,
K. S., 2024, Synthesis of Luminescent Copper Nanoparticles Using Couroupita
guianensis Flower Extract: Evaluation of Antibacterial and Anticancer
Activities. Luminescence, 39(10), e4913.
[28]. Abareethan, M.,
Sathiyapriya, R., Pavithra, M. E., Parvathy, S., Thirumalaisamy, R.,
Selvankumar, T., Almoallim, H. S., 2024, Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from
Solanum trilobatum Leaf Extract and Assessing their Antioxidant and
Antimicrobial Potential. Chemical Physics Impact, 100771.

