Effect of Natural Flavonoid Apigenin in Lowering High Glucose-Induced Insulin Resistance via Targeting PI3K/AKT Pathway in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes – Evidence Through an In-vitro and In-silico Approach
Abstract:
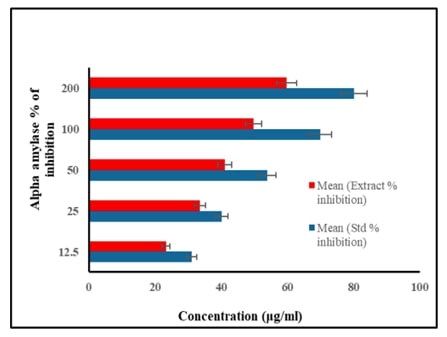
Diabetes mellitus, characterized by elevated blood glucose levels resulting from insulin deficiency or resistance, poses a significant global health challenge. With its increasing prevalence and substantial impact on morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs, effective strategies for managing diabetes are urgently needed. Natural flavonoid such as apigenin, has emerged as potential therapeutic agent due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory anti-diabetic properties but mechanism of action is not known. The study was aimed at assessing the role of apigenin on PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Invitro alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibitory activity was measured by spectrophotometric methods. Cytotoxicity was assessed by MTT assay. Further, gene expression analysis was done by Real Time-PCR. In order to confirm the exact binding interaction of apigenin with PI3K/Akt/GLUT4 signaling, molecular docking analysis was also performed. Results of this study showed that apigenin significantly reduced alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibitory activity in a dose-dependent fashion. q-PCR analysis showed that apigenin significantly improved mRNA expression of insulin signaling molecules (IR, IRS-1, PI3K, Akt and GLUT4) in high glucose-induced 3T3-L1 adipocytes cell line. Molecular docking analysis evidenced that apigenin confirmed possible role of apigenin that regulates insulin metabolic signaling in adipocytes. Overall, apigenin holds promise as a natural flavonoid with potential therapeutic value in combating diabetes and its complications, underscoring the importance of continued research to unlock its full therapeutic potential and pave the way for effective diabetes management strategies.References:
[1].
Salehi,
B., Venditti, A., Sharifi-Rad, M., Kręgiel, D., Sharifi-Rad, J., Durazzo, A.,
Lucarini, M., Santini, A., Souto, E. B., Novellino, E., Antolak, H., Azzini,
E., Setzer, W. N., & Martins, N., 2019, The Therapeutic Potential of
Apigenin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061305
[2].
Selvaraj,
J., Veeraraghavan,
V., Periyasamy,
V., and Rajagopal,
P., 2021., In Silico
and in Vitro Study on the Inhibition
of FtsZ Protein of Staphylococcus Aureus
by Active Compounds from Andrographis Paniculata.
Journal of Biologically Active Products
from Nature, 11(2): 116–128.
doi:10.1080/22311866.2021.1908163.
[3]. Ponnulakshmi, R., Shyamaladevi, B., Vijayalakshmi, P., &
Selvaraj, J., 2019, In silico and in vivo analysis to identify the
antidiabetic activity of beta sitosterol in adipose tissue of high fat diet and
sucrose induced type-2 diabetic experimental rats. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods, 29(4): 276–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2018.1545815.
[4].
Babu, S., Jayaraman, S., 2020, An update on β-sitosterol: A
potential herbal nutraceutical for diabetic management. Biomed Pharmacother,
131:110702. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110702.
Epub 2020 Aug 31. PMID: 32882583.
[5].
Jayaraman, S.,
Roy, A.,
Vengadassalapathy, S., Sekar,
R., Veeraraghavan,
V. P., Rajagopal, P.,
Rengasamy, G.,
Mukherjee, R.,
Sekar, D.,
Manjunathan, R., 2021, An Overview on the Therapeutic Function of Foods
Enriched with Plant Sterols in Diabetes Management. Antioxidants.; 10(12):1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10121903
[6].
Jayaraman, S.,
Devarajan, N.,
Rajagopal, P.,
Babu, S.,
Ganesan, S. K., Veeraraghavan,
V. P., Palanisamy, C. P., Cui,
B., Periyasamy,
V., Chandrasekar, K.,
2021, β-Sitosterol Circumvents Obesity Induced Inflammation and Insulin
Resistance by down-Regulating IKKβ/NF-κB and JNK Signaling Pathway in
Adipocytes of Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Molecules;
26(7):2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072101.
[7].
Pei, J., Yan, Y., Jayaraman, S., Rajagopal, P., Natarajan, P. M., Umapathy, V. R., Gopathy, S., Roy, J. R., Sadagopan, J. C., Thalamati, D., Palanisamy, C. P., Mironescu, M., 2024, A review on advancements in
the application of starch-based nanomaterials in biomedicine: Precision drug
delivery and cancer therapy. Int J Biol Macromol, 265(Pt 1):130746. doi:
10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130746. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38467219.
[8].
Jayaraman, S., Natarajan, S. R.,
Ponnusamy, B., Veeraraghavan, V. P., & Jasmine, S., 2023, Unlocking the potential of beta sitosterol: Augmenting the suppression of oral cancer cells
through extrinsic and intrinsic signalling mechanisms. The Saudi Dental Journal, 35(8): 1007-1013.
[9].
Hatano, T., Edamatsu, R., Hiramatsu, M., MORI, A., Fujita,
Y., Yasuhara, T., & OKUDA, T., 1989, Effects of the interaction of tannins
with co-existing substances. VI.: effects of tannins and related polyphenols on
superoxide anion radical, and on 1, 1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical. Chemical
and pharmaceutical bulletin, 37(8), 2016-2021.

