Polydatin: A Promising Natural Agent with Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Properties
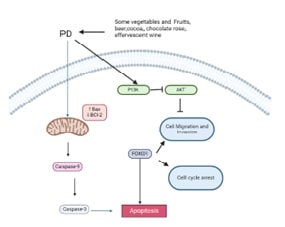
Abstract:
The review extensively examines the multifaceted anti-cancer properties
of polydatin (PD), a stilbenoid compound sourced from fruits and vegetables. PD
is known for its antioxidant capabilities, anti-inflammatory effects, and
anti-cancer properties. The analysis delves into PD's impact on cancer
characteristics such as cellular proliferation, metastasis, and apoptosis. It
highlights PD's potential as a targeted therapeutic agent and its synergistic
interactions with existing anti-cancer medications, aiming to enhance
understanding and innovative strategies in cancer therapy. Ultimately, this
review aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of PD's diverse anti-cancer
attributes and intrinsic value in advancing novel paradigms in cancer treatment
and prevention, instilling hope for the future of cancer therapy.
References:
[1].
Jun,
J.I., Lau, L.F., 2018, Resolution of organ fibrosis. Journal of Clinical
Investigation. 128(1):97-107. Doi:10.1172/JCI93563
[2].
Cheong,
K.L., Yu, B., & Teng, B., 2023, Post-COVID-19 syndrome management:
Utilizing the potential of dietary polysaccharides. Biomedicine &
Pharmacotherapy. 166(115320):115320. Doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115320
[3].
Cheong,
K.L., Chen, S., Teng, B., Veeraperumal, S., Zhong, S., & Tan. K., 2023,
Oligosaccharides as potential regulators of gut Microbiota and intestinal
health in post-COVID-19 management. Journal Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
16(6). Doi:10.3390/ph16060860.
[4].
Wang,
M., Veeraperumal, S., Zhong, S., & Cheong, K.L., 2023, Fucoidan-derived
functional oligosaccharides: Recent developments, preparation, and potential
applications. Foods. 12(4). Doi:10.3390/foods12040878
[5].
Tang,
C., Ding, R., Sun, J., Liu, J., & Kan, J., 2019, The impacts of natural
polysaccharides on intestinal microbiota and immune responses-a review.
Journal Food & Function is Food & Function. 10:2290-2312.
[6].
Zhang,
A., Wang, J., Hu, Y., Qiu, Y., & Dong, C., 2024, Polysaccharides play an
anti-fibrotic role by regulating intestinal flora: A review of research
progress. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 271(Pt
2):131982. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131982
[7].
Wang,
M., Lu, S., Zhao, H., Liu, Z., Sheng, K., & Fang, J., 2022, Natural
polysaccharides as potential anti-fibrotic agents: A review of their progress. Journal
Life Sciences. 308(120953):120953. Doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120953
[8].
Zhang,
L-Y LZ., 2020, Advances in the research of anti-organ fibrosis drugs. Acta Pharmaceutica
Sinica B. 2510-2528.
[9].
Zhao,
X., Chen, J., Sun, H., Zhang, Y., Zou, D., 2022, New insights into fibrosis
from the ECM degradation perspective: the macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction. Journal
Cell & Bioscience. 12(1):117. Doi:10.1186/s13578-022-00856-w
[10].
Rockey,
D.C., Bell, P.D., Hill, J.A., 2015, Fibrosis-a common pathway to organ injury
and failure. The New England Journal of Medicine. 372:1138-1149
[11].
Zhao,
M., Wang, L., Wang, M., Zhou, S., Lu, Y., 2022, Targeting fibrosis: Mechanisms
and clinical trials. Signal transduction and Targeted Therapy. 7
[12].
Kozawa,
S., Tejima, K., Takagi, S., 2023, Latent inter-organ mechanism of idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis unveiled by a generative computational approach. Scientific
Reports. 13(1):21981. Doi:10.1038/s41598-023-49281-0
[13].
Álvarez,
J., Real, J., Guarner, F., Gueimonde, M., Rodríguez, J.M., 2021, Microbiota
intestinal y salud. Gastroenterología y Hepatología. 44:519-535
[14].
Wu,
Y., Li, Y., Luo, Y., 2022, Gut microbiome and metabolites: The potential key
roles in pulmonary fibrosis. Frontiers in Microbiology. 13:943791. Doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.943791
[15].
Drakopanagiotakis,
F., Stavropoulou, E., Tsigalou, C., Nena, E., Steiropoulos, P., 2022 The role
of the microbiome in connective-tissue-associated interstitial lung disease and
pulmonary vasculitis. Biomedicines. 10(12):3195. Doi:10.3390/biomedicines10123195
[16].
Chioma,
O.S., Mallott, E.K., Chapman, A., 2022, Gut microbiota modulates lung fibrosis
severity following acute lung injury in mice. Communications Biology.
5(1):1401. Doi:10.1038/s42003-022-04357-x
[17].
Aydın,
M.M., Akçalı, K.C., 2018, Liver fibrosis. Turkish Journal of
Gastroenterology. 29(1):14-21. Doi:10.5152/tjg.2018.17330
[18].
Trautwein,
C., Friedman, S.L., Schuppan, D., Pinzani, M., 2015, Hepatic fibrosis: Concept
to treatment. Hepatology. 62(1 Suppl):S15-24. Doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.039
[19].
Friedman,
S.L., 2024, Hepatic fibrosis and cancer: The silent threats of metabolic
syndrome. Diabetes Metab J. 48(2):161-169. Doi:10.4093/dmj.2023.0240
[20].
Lee,
C.M., Yoon, E.L., Kim, M., 2024, Prevalence, distribution, and hepatic fibrosis
burden of the different subtypes of steatotic liver disease in primary care
settings. Hepatology. 79(6):1393-1400. Doi:10.1097/HEP.0000000000000664
[21].
Gao,
L.L., Ma, J.M., Fan, Y.N., 2021, Lycium barbarum polysaccharide combined with
aerobic exercise ameliorated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through restoring
gut microbiota, intestinal barrier and inhibiting hepatic inflammation. International
Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 183:1379-1392. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.066
[22].
Li
S. 2022. Investigation of the Anti-HF Mechanism of Taraxacum mongolicum
Polysaccharide With Astragalus Polysaccharide Via Gut–Liver Axis.
[23].
Shu,
Y., Huang, Y., Dong, W., 2023, The polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula
alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating gut microbiota and
bile acids metabolism. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.
246(125662):125662. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125662
[24].
Han,
C., Li, Z., Liu, R., 2023, Lonicerae flos polysaccharides improve nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease by activating the adenosine 5’-monophosphate-activated
protein kinase pathway and reshaping gut microbiota. Journal of the Science
of Food and Agriculture. 103(15):7721-7738. Doi:10.1002/jsfa.12854
[25].
Fang,
S., Wang, T., Li, Y., 2022, Gardenia jasminoides Ellis polysaccharide
ameliorates cholestatic liver injury by alleviating gut microbiota dysbiosis
and inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. International Journal of
Biological Macromolecules 205:23-36. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.056
[26].
Humphreys,
B.D., 2018, Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annual Review of Physiology.
80(1):309-326. Doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034227
[27].
Liu,
Y., 2011, Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nature
Reviews Nephrology. 7(12):684-696. Doi:10.1038/nrneph.2011.149
[28].
Nogueira,
A., Pires, M.J., Oliveira, P.A., 2017, Pathophysiological mechanisms of renal
fibrosis: A review of animal models and therapeutic strategies. In Vivo.
31(1):1-22. Doi:10.21873/invivo.11019
[29].
Yang,
J., Dong, H., Wang, Y., 2020, Cordyceps cicadae polysaccharides ameliorated
renal interstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy rats by repressing
inflammation and modulating gut microbiota dysbiosis. International Journal
of Biological Macromolecules. 163:442-456. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.153
[30].
Zhang,
M., Yang, L., Zhu, M., 2022, Moutan Cortex polysaccharide ameliorates diabetic
kidney disease via modulating gut microbiota dynamically in rats. International
Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 206:849-860. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.077
[31].
Feng,
Y., Weng, H., Ling, L., 2019, Modulating the gut microbiota and inflammation is
involved in the effect of Bupleurum polysaccharides against diabetic
nephropathy in mice. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 132:1001-1011.
Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.242
[32].
Liu,
J.X., Yuan, H.Y., Li, Y.N., Wei, Z., Liu, Y., Liang, J., 2022, Ephedra sinica
polysaccharide alleviates airway inflammations of mouse asthma-like induced by
PM2. 5 and ovalbumin via the regulation of gut microbiota and short chain fatty
acid. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 74:1784-1796.
[33].
Shi,
C., Zhou, L., Li, H., 2022, Intestinal microbiota metabolizing Houttuynia
cordata polysaccharides in H1N1 induced pneumonia mice contributed to Th17/Treg
rebalance in gut-lung axis International Journal of Biological
Macromolecules. 221:288-302. Doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.015
[34].
Long,
H.Z., Cheng, Y., Zhou, Z.W., Luo, H.Y., Wen, D.D., Gao, L.C., 2021, PI3K/AKT
Signal Pathway: A Target of Natural Products in the Prevention and Treatment of
Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease. Frontiers in Pharmacology.
12:648636. Doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.648636

