Association of Microalbuminuria in Patient with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study in A Tertiary Care Centre
Abstract:
NAFLD (Nonalcoholic Fatty
Liver Disease) is a prevalent chronic liver disorder characterized by metabolic
abnormalities. Microalbuminuria have been linked to cardiovascular and renal
diseases, but its association with NAFLD remains underexplored. This
cross-sectional study assessed urine microalbumin levels in patients diagnosed
with NAFLD. Demographic data, NAFLD grading, and microalbuminuria status were
analyzed in non-NAFLD and NAFLD groups. Statistical analysis has been performed
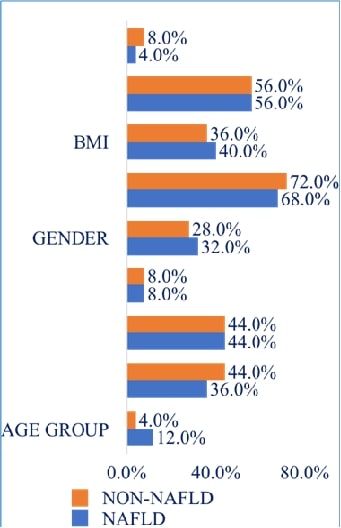
to evaluate the associations. Males were more common than females among NAFLD
patients (n=100), particularly in the age range of 41 to 60. Compared to
non-NAFLD controls (0%), NAFLD patients (76%) had a considerably higher
prevalence of microalbuminuria. BMI showed no significant association with
NAFLD prevalence. NAFLD grading revealed Grade 1 as the most prevalent (52%),
followed by Grade 2 (32%) and Grade 3 (16%). Our findings demonstrate a strong
association between microalbuminuria and NAFLD, suggesting a potential link
with adverse cardiovascular and renal outcomes. Monitoring microalbuminuria in
NAFLD patients may aid in risk stratification and management. There is a need
to conduct larger population-based-randomized studies.
References:
[1]. Nascimbeni F, Pais R, Bellentani S, Day CP, Ratziu V,
Loria P, et al. From NAFLD in clinical practice to answers from guidelines. J
Hepatol. 2013;59: 859–871.
[2]. Leoni S, Tovoli F, Napoli L, Serio I, Ferri S, Bolondi L.
Current guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A
systematic review with comparative analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:
3361–3373.
[3]. Lr SG, Dhande SK, Kv R, M J. Correlation between severity
of thrombocytopenia and portal hypertensive gastropathy in patients with
chronic liver disease. J Assoc Physicians India. 2023;71: 1.
[4]. Kadiyala V, Savitha G. Assessment of Gamma Glutamyl
Transferase in Chronic Periodontitis. Research Journal of Pharmacy and
Technology. 2018;11: 5083–5085.
[5]. Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF).
AISF position paper on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Updates and
future directions. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49: 471–483.
[6]. Lonardo A, Nascimbeni F, Mantovani A, Targher G.
Hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis and NASH: Cause or consequence? J
Hepatol. 2018;68: 335–352.
[7]. Petersen KF, Dufour S, Feng J, Befroy D, Dziura J, Dalla
Man C, et al. Increased prevalence of insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease in Asian-Indian men. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:
18273–18277.
[8]. Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L,
Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta‐analytic
assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64: 73–84.
[9]. Tha TP, Saveetha Dental College and Hospital, Chennai,
Tamilnadu, India. Non-pharmacological treatment for non alcoholic fatty liver
DiseaseA review. J Med Sci Clin Res. 2016. doi:10.18535/jmscr/v4i8.61.
[10]. Lee YH, Cho Y, Lee BW, Park CY, Lee DH, Cha BS, et al.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetes. Part I: Epidemiology and
diagnosis. Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43: 31–45.
[11]. Han E, Kim MK, Jang BK, Kim HS. Albuminuria is associated
with steatosis burden in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45: 698–707.
[12]. Lonardo A, Ballestri S, Marchesini G, Angulo P, Loria P.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a precursor of the metabolic syndrome. Dig
Liver Dis. 2015;47: 181–190.
[13]. Ahn SH, Seo DH, Kim SH, Nam M-S, Hong S. The relationship
between fatty liver index and bone mineral density in Koreans: KNHANES
2010–2011. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29: 181–190.
[14]. Petta S, Valenti L, Bugianesi E, Targher G, Bellentani S,
Bonino F, et al. A “systems medicine” approach to the study of non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2016;48: 333–342.
[15]. Targher G, Byrne CD, Lonardo A, Zoppini G, Barbui C.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident cardiovascular disease:
A meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2016;65: 589–600.
[16]. Becker GJ, Wheeler DC, De ZD, Fujita T, Furth SL, Holdaas
H, et al. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) blood pressure work
group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure
in chronic kidney disease. Kidney International Supplements. 2012;2: 337–414.
[17]. Lieb W, Mayer B, Stritzke J, Doering A, Hense H-W, Loewel
H, et al. Association of low-grade urinary albumin excretion with left
ventricular hypertrophy in the general population: the MONICA/KORA Augsburg
Echocardiographic Substudy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21: 2780–2787.
[18]. Tanaka F, Komi R, Makita S, Onoda T, Tanno K, Ohsawa M,
et al. Low-grade albuminuria and incidence of cardiovascular disease and
all-cause mortality in nondiabetic and normotensive individuals. J Hypertens.
2016;34: 506–12; discussion 512.
[19]. Currie G, McKay G, Delles C. Biomarkers in diabetic
nephropathy: Present and future. World J Diabetes. 2014;5: 763–776.
[20]. Kim J-J, Hwang B-H, Choi IJ, Choo E-H, Lim S, Koh Y-S, et
al. A prospective two-center study on the associations between
microalbuminuria, coronary atherosclerosis and long-term clinical outcome in
asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: evaluation by coronary CT
angiography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;31: 193–203.
[21]. Kasapoglu B, Turkay C, Yalcın KS, Boga S, Bozkurt A.
Increased microalbuminuria prevalence among patients with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Ren Fail. 2016;38: 15–19.
[22]. Kim H, Kim HJ, Shin N, Han M, Park H, Kim M, et al.
Visceral obesity is associated with microalbuminuria in nondiabetic Asians.
Hypertens Res. 2014;37: 679–684.
[23]. Amorim R, Soares P, Chavarria D, Benfeito S, Cagide F,
Teixeira J, et al. Decreasing the burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
From therapeutic targets to drug discovery opportunities. Eur J Med Chem.
2024;277: 116723.
[24]. Balamithra S, Devi RG, Jyothipriya A. Estimation of
gamma-glutamyl transferase level in liver cancer patients. Drug Invention
Today. 2019;12: 1781–1783.
[25]. Mahmoud HE-DA, Yousry WA, Saleh SA, El Badry M, Hussein
A, Ali MH, et al. Renal resistive index in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as
an indicator of early renal affection. Egypt Liver J. 2020;10.
doi:10.1186/s43066-019-0006-7.
[26]. Wang Y, Fang Y. Postabsorptive homeostasis model
assessment for insulin resistance is a reliable biomarker for cardiovascular
disease mortality and all-cause mortality. Diabet Epidemiol Manag. 2022;6:
100045.
[27]. Lingli X, Qing Z, Wenfang X. Diagnostic value of the
Modification of Diet in Renal Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology
Collaboration equations in diabetic patients: a systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2020;48: 300060520925950.
[28]. Saverymuttu SH, Joseph AE, Maxwell JD. Ultrasound
scanning in the detection of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis. BMJ. 1986;292:
13–15.
[29]. Perdomo CM, Garcia-Fernandez N, Escalada J. Diabetic
kidney disease, cardiovascular disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A
new triumvirate? J Clin Med. 2021;10: 2040.
[30]. Carulli L, Lonardo A, Lombardini S, Marchesini G, Loria
P. Gender, fatty liver and GGT. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). Ovid Technologies
(Wolters Kluwer Health); 2006. pp. 278–279.
[31]. El Azeem HA, Khalek E-SA, El-Akabawy H, Naeim H, Khalik
HA, Alfifi AA. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the
incidence of cardiovascular and renal events. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2013;25:
239–246.
[32]. Hwang ST, Cho YK, Yun JW, Park JH, Kim HJ, Park DI, et
al. Impact of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on microalbuminuria in patients
with prediabetes and diabetes. Intern Med J. 2010;40: 437–442.
[33]. Targher G, Chonchol MB, Byrne CD. CKD and nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64: 638–652.
[34]. Mantovani A, Zaza G, Byrne CD, Lonardo A, Zoppini G,
Bonora E, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease increases risk of incident
chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism.
2017;79: 64–76.

