Case Series of Comminuted Fractures of Proximal Tibia with Ligament Injuries Treated with Knee Spanning Ilizarov Fixation
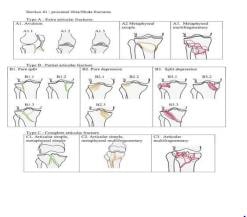
Abstract:
Comminuted
fractures of the tibial plateau with intra-articular extension and ligament
injuries are caused by high-energy trauma. The associated high rate of soft
tissue injuries leads to complications like joint stiffness, compartment
syndrome, malunion, skin loss, osteomyelitis, knee contractures, and potential
amputation. The knee-spanning Ilizarov external fixator minimizes these
complications by allowing early mobilization and weight-bearing, reducing soft
tissue injury and blood loss, and providing stable fixation. Assessment using
the Knee Society Score pre- and post-operatively showed improvement. This
prospective study includes 15 patients with comminuted tibial intra-articular
fractures and associated ligament injuries, treated with knee-spanning Ilizarov
fixation. Clinical and radiological assessments post-procedure indicated
positive outcomes. Out of 15 patients, 80% achieved good clinical and
radiological outcomes, including early mobilization, normal gait, and
successful fracture healing. Complications included pin tract infections (2
patients), knee stiffness (1 patient), and secondary procedures such as
arthrodesis and TKR due to arthritis.
References:
[1].
Rockwood, C., Green, D., 2006, Fractures
in Adults, 6th ed., Volume 2, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins.
[2].
Joveniaux, P., Ohl, X., Harisboure, A.,
Berrichi, A., Labatut, L., Simon, P., Mainard, D., Vix, N., Dehoux, E., 2010,
Distal tibia fractures: management and complications of 101 cases, International
Orthopaedics, 34(4), pp. 583-588, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0832-z
[3].
Dillin, L., Slabaugh, P., 1986, Delayed
wound healing, infection, and non-union following open reduction and internal
fixation of tibial plafond fractures, Journal of Trauma, 26(12), pp.
1116-1119.
[4].
McFerran, M. A., Smith, S. W., Boulas, H. J.,
Schwartz, H. S., 1992, Complications encountered in the treatment of pilon
fractures, Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 6(2), pp. 195-200.
[5].
Teeny, S. M., Wiss, D. A., 1993, Open
reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures: variables
contributing to poor results and complications, Clinical Orthopaedics and
Related Research, 292, pp. 108-117.
[6].
Tull, F., Borrelli, J., 2003, Soft-tissue
injury associated with closed fractures: evaluation and management, Journal
of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 11, pp. 431-438.
[7].
Sirkin, M., Sanders, R., DiPasquale, T.,
Herscovici, D., 2004, A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the
treatment of complex pilon fractures, Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma,
18(Suppl 8), pp. S32-S38.
[8].
Dickson, K. F., Montgomery, S., Field, J.,
2001, High energy plafond fractures treated by a spanning external fixator
initially and followed by a second stage open reduction internal fixation of
the articular surface—preliminary report, Injury, 32(Suppl 4), pp.
92-98.
[9].
Mauffrey, C., Vasario, G., Battiston, B.,
Lewis, C., Beazley, J., Seligson, D., 2011, Tibial pilon fractures: a review of
incidence, diagnosis, treatment, and complications, Acta Orthopaedica
Belgica, 77, pp. 432-440.
[10]. Zelle,
B., Bhandari, M., Espiritu, M., Koval, K., Zlowodzki, M., 2006, Treatment of
distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of
1125 fractures, Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 20(1), pp. 76-79.
[11]. Robinson,
C. M., McLauchlan, G. J., McLean, I. P., Court-Brown, C. M., 1995, Distal
metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle:
classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing, Journal of
Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume, 77-B, pp. 781-787.
[12]. Casstevens,
C., Le, T., Archdeacon, M. T., Wyrick, J. D., 2012, Management of
extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: intramedullary nailing versus
plate fixation, Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,
20(11), pp. 675-683.
[13]. Newman,
S. D., Mauffrey, C. P., Krikler, S., 2011, Distal metadiaphyseal tibial
fractures, Injury, 42(10), pp. 975-984.
[14]. Tornetta,
P. III, Weiner, L., Bergman, M., Watnik, N., Steuer, J., Kelly, M., Yang, E.,
1993, Pilon fractures: treatment with combined internal and external fixation, Journal
of Orthopaedic Trauma, 7(6), pp. 489-496.
[15]. Wrysch,
B., McFerran, M. A., McAndrew, M., Limbird, T. J., Harper, M. C., Johnson, K. D.,
Schwartz, H. S., 1996, Operative treatment of fractures of the tibial plafond:
a randomized, prospective study, Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American
Volume, 78(11), pp. 1646-1657.
[16]. Ristiniemi,
J., Flinkkila, T., Hyvonen, P., Lakovaara, M., Pakarinen, H., Jalovaara, P.,
2007, RhBMP-7 accelerates the healing in distal tibial fractures treated by
external fixation, Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British Volume,
89(2), pp. 265-272.
[17]. Barbieri,
R., Schenk, R., Koval, K., Aurori, K., Aurori, B., 1996, Hybrid external
fixation in the treatment of tibial plafond fractures, Clinical Orthopaedics
and Related Research, 332, pp. 16-22.
[18]. McDonald,
M. G., Burgess, R. C., Bolano, L. E., Nicholls, P. J., 1996, Ilizarov treatment
of pilon fractures, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 325, pp.
232-238.
[19]. Lovisetti,
G., Agus, M. A., Pace, F., Capitani, D., Sala, F., 2009, Management of distal
tibial intra-articular fractures with circular external fixation, Strategies
in Trauma and Limb Reconstruction, 4(1), pp. 1-6.
[20]. 20. Vasiliadis, E. S., Grivas, T. B., Psarakis, S. A., Evangelos, P., Kaspiris, A., Triantafyllopoulos, G., 2009, Advantages of the Ilizarov external fixation in the management of intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia, Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 4, pp. 35, https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-4-35

