Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Pyocyanin Production from Multidrug Resistance P. aeruginosa by Using Vitamin C, Salicylic Acid, and Multisera
Abstract:
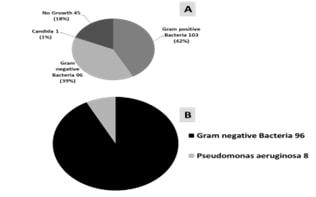
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a potent
nosocomial pathogen, causing several infections, mostly urinary tract
infections (UTIs). The present study is thus aimed to detect the susceptibility
pattern of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to antibiotics from urine specimens, and virulence
factor production such as (biofilm, and pyocyanin) which are regulated by
quorum sensing. The aims were extended to detect the Inhibition of Biofilm
formation and pyocyanin production by using vitamin C, salicylic acid and Multi
sera. A total of 245 samples were collected from the
patients. The samples were subjected to inoculation, isolation and
identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa which were 8 (4%) from total isolates,
by standard microbiological procedures. Confirmation of isolates was done by polymerase chain
reaction targeting 16srRNA.
Antimicrobial sensitivity testing was done using the modified
Kirby-Bauer method of the disc diffusion test, with high
resistance rates against ceftriaxone (100%) while high sensitivity was to meropenem
(88%). Quorum
sensing Genes (lasl, lasR) were also detected in Multi-drug resistance and pan
resistance isolates. In general, all isolates were Biofilm formation and
pyocyanin production. The highest Inhibition of Biofilm was by using vitamin C
while the highest
Inhibition of pyocyanin was by using salicylic
acid.
References:
[1]. Stover, C. K., Pham, X. Q., Erwin,
A. L., Mizoguchi, S. D., Warrener, P., Hickey, M. J., Olson, M. V., 2000,
Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an
opportunistic pathogen. Nature, 406(6799), 959-964,
doi:10.1038/35023079.
[2]. Ito, C. A. S., Bail, L., Arend, L. N.
V. S., Nogueira, K. D. S., Tuon, F. F., 2021, The activity of
ceftazidime/avibactam against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Infectious Diseases, 53(5), 386-389, doi:10.1080/23744235.2020.1867763.
[3]. Turkina, M. V., Vikström, E., 2019,
Bacteria-host crosstalk: sensing of the quorum in the context of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa infections. Journal of Innate Immunity, 11(3), 263-279,
doi:10.1159/000494069.
[4]. Alkhulaifi, M. M., 2017, Using
Phage’s to exterminate biofilms. Journal of Medical Microbiology and
Diagnosis, 259(6):1-5, doi:10.4172/2161-0703.1000259.
[5]. Duplantier, M., Lohou, E., Sonnet,
P., 2021, Quorum sensing inhibitors to quench P. aeruginosa pathogenicity.
Pharmaceuticals, 14(12), 1-35, doi:10.3390/ph14121262.
[6]. El-Fouly, M. Z., Sharaf, A. M.,
Shahin, A. A. M., El-Bialy, H. A., Omara, A. M. A., 2015, Biosynthesis of
pyocyanin pigment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Radiation
Research and Applied Sciences, 8(1), 36-48, doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2014.10.007.
[7]. Wang, T., Sun, W., Fan, L., Hua,
C., Wu, N., Fan, S., Yan, J., 2021, An atlas of the binding specificities of
transcription factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa directs prediction of
novel regulators in virulence. Elife, 10, e61885,1-25,
doi:10.7554/eLife.61885.
[8]. Jayaseelan, S., Ramaswamy, D.,
Dharmaraj, S., 2014, Pyocyanin: production, applications, challenges and new
insights. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 1159-1168,
doi:10.1007/s11274-013-1552-5.
[9]. Shouman, H., Said, H. S., Kenawy,
H. I., Hassan, R., 2023, Molecular and biological characterization of pyocyanin
from clinical and environmental Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbial
Cell Factories, 22(1), 166, doi:10.1186/s12934-023-02169-0.
[10]. Yin, W. F., Purmal, K., Chin, S.,
Chan, X. Y., Koh, C. L., Sam, C. K., Chan, K. G., 2012, N-acyl homoserine
lactone production by Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from human tongue
surface. Sensors, 12(3), 3472-3483, doi:10.3390/s120303472.
[11]. Zhao, X., Yu, Z., Ding, T., 2020,
Quorum-sensing regulation of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Microorganisms,
8(3), 1-21, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8030425.
[12]. Chourasiya, S. S., Kathuria, D.,
Singh, S., Sonawane, V. C., Chakraborti, A. K., Bharatam, P. V., 2015, Design,
synthesis and biological evaluation of novel unsymmetrical azines as quorum
sensing inhibitors. RSC advances, 5(97), 80027-80038,
doi:10.1039/C5RA12925G.
[13]. Abdel Bar, F. M., Alossaimi, M. A.,
Elekhnawy, E., Alzeer, M. A. A., Abo Kamer, A., Moglad, E., ElNaggar, M. H.,
2022, Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of Pelargonium× hortorum
root extract against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Combinatorial effect of
catechin and gallic acid. Molecules, 27(22), 7841, doi:10.3390/molecules27227841.
[14]. Piecuch, A., Lamch, Ł., Paluch, E.,
Obłąk, E., Wilk, K. A., 2016, Biofilm prevention by dicephalic cationic
surfactants and their interactions with DNA. Journal of Applied Microbiology,
121(3), 682-692, doi:10.1111/jam.13204.
[15]. Kamaruzzaman, N. F., Tan, L. P.,
Mat Yazid, K. A., Saeed, S. I., Hamdan, R. H., Choong, S. S., Gibson, A. J.,
2018, Targeting the bacterial protective armour; challenges and novel
strategies in the treatment of microbial biofilm. Materials, 11(9),1-27,
doi:10.3390/ma11091705.
[16]. Abdulhaq, N., Nawaz, Z., Zahoor, M.
A., Siddique, A. B., 2020, Association of biofilm formation with multi drug
resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. EXCLI Journal,
19(1), 201-208, doi:10.17179/EXCLI2019-2049.
[17]. Khaleel, A. M., Faisal, R. M.,
Altaii, H. A., 2023, The efficiency of molecular methods compared to
traditional methods in identifying bacteria from blood and cerebrospinal fluid
samples. Malaysian Journal of Microbiology, 19(2):1-10,
doi:10.21161/mjm.220105.
[18]. Khalid, I., Nayyef, N. S., Merkhan,
M. M., 2022, A Taxonomic Study comparing the two types of Medicinal Leeches
available in Iraq. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 15(3),
1119-1122, doi:10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00187.
[19]. Humphries, R., Bobenchik, A. M.,
Hindler, J. A., Schuetz, A. N., 2021, Overview of changes to the clinical and
laboratory standards institute performance standards for antimicrobial
susceptibility testing, M100. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 59(12),
10-1128, doi:10.1128/JCM.00213-21.
[20]. Sultan, A. M., Amer, G. F., Nabiel,
Y., 2021, Quinolone-resistant uropathogenic E. coli: is there a relation
between qnr genes, gyrA gene target site mutation and biofilm formation? Journal
of Medical Microbiology, 70(10), 001432, doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001432.
[21]. Lahij, H. F., Alkhater, A. H.,
Hassan, M. H., Yassir, L. A., 2021, The Effect of Qourum Sensing genes (lasI,
rhlI) in Some Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from
Different Clinical Sources. Medico-legal Update, 21(1),303-308,
doi:10.37506/mlu. v21i1.2325.
[22]. Mansuri, A., Lokhande, K., Kore,
S., Gaikwad, S., Nawani, N., Swamy, K. V., Pawar, S., 2022, Antioxidant,
anti-quorum sensing, biofilm inhibitory activities and chemical composition of
Patchouli essential oil: in vitro and in silico approach. Journal
of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(1), 154-165,
doi:10.1080/07391102.2020.1810124.
[23]. Farhadi, Z., Bahador, N., 2018,
Pathotypic and phylogenetic studies of urine Escherichia coli isolates
from girls< 5 years of age in Marvdasht hospital. Biomedical and
Biotechnology Research Journal (BBRJ), 2(4), 281-285, doi: 10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_73_18.
[24]. AL-Khikani, F. H. O., Ayit, A. S.,
2019, Correlation study between urinary tract bacterial infection and some
acute inflammatory responses. Biomedical and Biotechnology Research Journal
(BBRJ), 3(4), 236-239, doi: 10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_122_19.
[25]. Kassob, D. S., Hummadi, E. H.,
2023, Study of pyocyanin production and biofilm formation in clinical Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Academic Science Journal, 1(2),139-152,
doi:10.24237/ASJ.01.02.648B.
[26]. Abbas, R., Nawaz, Z., Siddique, A. B.,
Aslam, R., Rafique, A., Zahoor, M. A., Alsayeqh, A. F., 2022, Molecular
Detection of Biofilm Production among Multidrug Resistant Isolates of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa from Meat Samples. Pakistan Veterinary Journal, 42(4), 505-510,
doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2022.074.
[27]. Tenover, F. C., Nicolau, D. P.,
Gill, C. M., 2022, Carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa–an
emerging challenge. Emerging Microbes & Infections, 11(1), 811-814,
doi:10.1080/22221751.2022.2048972.
[28]. Stultz, J. S., Arnold, S. R.,
Shelton, C. M., Bagga, B., Lee, K. R., 2019, Antimicrobial stewardship impact
on Pseudomonas aeruginosa susceptibility to meropenem at a tertiary
pediatric institution. American Journal of Infection Control, 47(12),
1513-1515, doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.05.001.
[29]. Shravani, V., Selvi, G. A. S.,
Mantravadi, H., 2023, Detection of quorum sensing virulence factor genes and
its consanguinity to antibiotic sensitivity profile in the clinical isolates of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences,
26(8), 899: 899-905, doi:10.22038/ijbms.2023.67981.14992.
[30]. Halim, R. M. A., Kassem, N. N.,
Mahmoud, B. S., 2018, Detection of biofilm-producing staphylococci among
different clinical isolates and its relation to methicillin susceptibility.
Open access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 6(8),1335–1341,
doi:10.3889/oamjms.2018.246.
[31]. Mohsenzadeh, A., Fazel, A., Bavari,
S., Borji, S., Pourasghar, S., Azimi, T., Sabati, H., 2021, Detecting of
biofilm formation in the clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
Escherichia coli: an evaluation of different screening methods. Journal of
Current Biomedical Reports, 2(2), 56-61, doi:10.52547/JCBioR.2.2.56.
[32]. Siddhiqui, S., Afreen, U., Kotgire,
S., 2018, Evaluation of biofilm formation by three different methods and its
antibiogram with special reference to indwelling medical devices from a
tertiary care hospital. Annals of Laboratory Medicine, 5(2), 171-76,
doi:10.21276/APALM.1630.
[33]. Padayatty, S. J., Levine, M., 2016,
Vitamin C: the known and the unknown and Goldilocks. Oral Diseases,
22(6), 463-493, doi:10.1111/odi.12446.
[34]. Pandit, S., Ravikumar, V.,
Abdel-Haleem, A. M., Derouiche, A., Mokkapati, V. R. S. S., Sihlbom, C.,
Mijakovic, I., 2017, Low concentrations of vitamin C reduce the synthesis of
extracellular polymers and destabilize bacterial biofilms. Frontiers in
microbiology, 8(1), 1-11, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.02599.
[35]. Das, T., Kutty, S. K., Tavallaie,
R., Ibugo, A. I., Panchompoo, J., Sehar, S., Manefield, M., 2015, Phenazine
virulence factor binding to extracellular DNA is important for Pseudomonas
aeruginosa biofilm formation. Scientific Reports, 5(1):1-9,
doi:10.1038/srep08398.
[36]. Lee, J., Zhang, L., 2015, The
hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein and
Cell, 6(1), 26-41, doi:10.1007/s13238-014-0100-x.
[37]. Han, B., Zheng, X., Baruah, K.,
Bossier, P., 2020, Sodium ascorbate as a quorum-sensing inhibitor leads to
decreased virulence in Vibrio campbellii. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11,
1054, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01054.
[38]. Das, T., Das, B., Young, B. C.,
Aldilla, V., Sabir, S., Almohaywi, B., Kumar, N., 2023, Ascorbic acid modulates
the structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor pyocyanin
and ascorbic acid-furanone-30 combination facilitate biofilm disruption. Frontiers
in Microbiology, 14(1),1-15, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1166607.
[39]. Lattab, A., Rachid, D., Arabi, A.,
Hichem, D., Com, A. Y., 2017, Effect of salicylic acid on biofilm formation and
on some virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International
Journal of Biosciences, 10, 60-71, doi:10.12692/ijb/10.1.60-71.
[40]. Yang, L., Rybtke, M. T., Jakobsen,
T. H., Hentzer, M., Bjarnsholt, T., Givskov, M., Tolker-Nielsen, T., 2009,
Computer-aided identification of recognized drugs as Pseudomonas aeruginosa
quorum-sensing inhibitors. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 53(6),
2432-2443, doi:10.1128/AAC.01283-08.
[41]. Prithiviraj, B., Bais, H. P., Jha,
A. K., Vivanco, J. M., 2005, Staphylococcus aureus pathogenicity on Arabidopsis
thaliana is mediated either by a direct effect of salicylic acid on the
pathogen or by SA‐dependent, NPR1‐independent host responses. The Plant
Journal, 42(3), 417-432, doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02385. x.
[42]. Guo, M., Gamby, S., Zheng, Y.,
Sintim, H. O., 2013, Small molecule inhibitors of AI-2 signalling in bacteria:
state-of-the-art and future perspectives for anti-quorum sensing agents. International
Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(9), 17694-17728,
doi:10.3390/ijms140917694.
[43]. Aybey, A., Demirkan, E., 2016,
Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and motilities by
human serum paraoxonase (hPON1). AIMS Microbiology, 2(4), 388-401,
doi:10.3934/microbiol.2016.4.388.
[44]. Khatun, M. A., Hoque, M. A.,
Koffas, M., Feng, Y., 2023, Reducing the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
by using multiple quorum-quenching enzymes. Journal of Industrial
Microbiology and Biotechnology, 50(1), kuad028, doi:10.1093/jimb/kuad028.

