Post-Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of Common Digital Artery of Superficial Palmar Arch- A Curious Case with Critical Complexities
Abstract:
Pseudoaneurysm
is an extremely rare condition but poses significant challenges in early
diagnosis and can lead to devastating complications if untreated. Pseudoaneurysm
is defined as the dilation of the arterial wall caused by disruption of the vessel
wall leading to extravasation of blood into a false sac that has communication
with the vessel lumen. True aneurysm is formed by all three layers of the arterial
wall while pseudoaneurysm is formed by tunica adventitia. Trauma is the most
common cause of pseudoaneurysms. It is a rare entity but with significant
complications such as thrombosis, embolism and compression of nerves and veins.
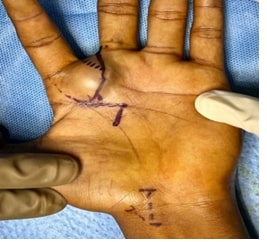
Here we bring up a case of a twenty-one-year-old male who presented with
swelling over his left hand below 2nd web space following a fire
crack injury which was associated with pain, restriction of movement and
numbness over his left middle finger. The swelling was found to be well-defined,
pulsatile, compressible, and cystic in consistency with palpable thrill and
systolic bruit on auscultation. Doppler ultrasound showed a cystic lesion with
characteristic yin-yang flow. A diagnosis of possible partially thrombosed
post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm was made. Surgical ligation with excision under
regional anaesthesia was done. Histopathological examination confirmed the
diagnosis of pseudoaneurysm. The patient made a full recovery with no post-operative
complications. This emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and management
of pseudoaneurysm. Also, this reinvigorates surgical management as the gold
standard treatment.
References:
[1].
Schoretsanitis, N.,
Moustafa, E., Beropoulis, E., Argyriou, C., Georgiadis, G. S., Georgakarakos, E,
2015, Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
and Review of the Literature. J Hand Microsurg. Jun;7(1):230-2. https://doi.org/10.1007/12593-015-0183-5
[2].
Fields, J. M., Chandra,
S., Au, A. K., Rotte, M., Ku, B. S., 2013, Images in emergency medicine. Child
with painful palmar mass. Superficial palmar arch pseudoaneurysm. Ann
Emerg Med.;62(6):569-577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.05.007
[3].
Maertens, A., Tchoungui
Ritz, F. J., Poumellec, M. A., Camuzard, O., Balaguer, T., 2020, Posttraumatic
pseudoaneurysm of a superficial branch of the ulnar artery: A case report. Int
J Surg Case Rep. 75:317-321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.09.029
[4].
Dell'Orfano,
M., Milella, F. M., Braidotti, P., 2023, Radial artery pseudoaneurysm following
wrist trauma. A case report of a rare condition. Trauma Case Rep 6; 44:100783.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcr.2023.100783
[5].
Gull,
S., Spence, R. A., Loan, W., 2011, Superficial palmar arch aneurysm after
carpal tunnel decompression, a rare complication: a case report. Case Rep
Med. 2011:595120. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/595120
[6].
Zitsman, J. L., 1998,
Pseudoaneurysm after penetrating trauma in children and adolescents. J
Pediatr Surg.;33(10):1574-1577. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3468(98)90504-8
[7].
Sakamoto, A., Arai, K.,
2009, False aneurysm of the superficial palmar arch in a child: A case report. Cases
J. 2009 Jul 24; 2:7985. https://doi.org/10.4076%2F1757-1626-2-7985
[8].
Kwiecien,
G. J., Garbuzov, A., Boonipat, T., Houdek, M. T., Moran, S. L., 2022,
Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Palmar Arch in a 6-month-old Child: A Case
Report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open;10(2): e4093. https://doi.org/10.1097%2FGOX.0000000000004093
[9].
Corvino,
A., Catalano, O., de Magistris, G., Corvino, F., Giurazza, F., Raffaella, N.,
Vallone, G., 2020, Usefulness of doppler techniques in the diagnosis of
peripheral iatrogenic pseudoaneurysms secondary to minimally invasive
interventional and surgical procedures: Imaging findings and diagnostic
performance study. J Ultrasound, 23(4):563-573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-020-00475-6
[10].
Papatheodorou,
N., Dimitriadis, K., Doukas, D., Argyriou, C., Georgiadis, G. S., 2022,
Surgical Reconstruction of Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of Palmar Arch Caused by
Blunt Trauma. Vasc Specialist Int 13; 38: 30. https://doi.org/10.5758/vsi.220031
[11].
Yadav,
R., Sharma, A., Pathak, S., 2023, Successful Surgical Management of
Post-traumatic Superficial Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm with Delayed
Presentation. Cureus. 15(9):e45739. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.45739
[12]. Mahmoud, M. Z., Al-Saadi, M.,
Abuderman, A., et al, 2015, "To-and-fro" waveform in the diagnosis of
arterial pseudoaneurysms. World Journal of Radiology.7(5):89-99. https://doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i5.89
[13].
Igari, K., Kudo, T.,
Toyofuku., T, Jibiki, M., Inoue, Y., 2013, Surgical treatment of aneurysms in
the upper limbs. Ann Vasc Dis;6(3):637-41. https://doi.org/10.3400/avd.cr.13-00024
[14].
Woodley-Cook, J.,
Konieczny, M., Simons, M., 2015, The ulnar artery pseudoaneurysm. BMJ Case
Rep. 2015 Oct 6;2015: https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2015-212791
[15].
Cozzi, D. A., Morini, F.,
Casati, A., Pacilli, M., Salvini, V., Cozzi, F., 2013, Radial artery
pseudoaneurysm successfully treated by compression bandage. Arch Dis
Child.;88(2):165-166. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.88.2.165
[16].
Muir, H., Cowan, K.,
Steele, P., Downie, J. J., 2021, Presentation and surgical management of a
superficial temporal artery pseudoaneurysm: A case report. Int J Surg Case
Rep. 79:368-370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.01.072
[17].
Wang,
Y., Zheng, H., Yao, W., Ju, S., Bai, Y., Wang, C., Zhou, C., Liu, J., Yang, C.,
Huang, S., Li, T., Chen, Y., Xiong, B., 2022, Management of traumatic
peripheral artery pseudoaneurysm: A 10-year experience at a single center. J
Interv Med;6(1):29-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jimed.2022.10.002
[18].
Shreve,
L., Jarmakani, M., Javan, H., Babin, I., Nelson, K., Katrivesis, J., Lekawa, M.,
Kuncir, E., Fernando, D., Abi-Jaoudeh, N., 2020, Endovascular management of
traumatic pseudoaneurysms. CVIR Endovasc;3(1):88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42155-020-00182-7
[19].
Saydam,
O., Serefli, D., Engin, A. Y., Atay, M., 2020, Ultrasound-guided thrombin
injection for treatment of iatrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysms compared
with open surgery: First experiences from a single institution. Ann Surg
Treat Res. 98(5):270-276. https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2020.98.5.270
[20]. Hughes, C. D., Binette,
C., Babigian, A., 2012, Pseudoaneurysm in the hand of a three-year-old boy: A case
report. J Emerg Med. 42(4):e87-e89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.11.049
[21].
Lucchina,
S., Nistor, A., Stricker, H., Fusetti, C., 2011, False aneurysm of the common
digital artery. Is reconstruction with an arterial graft worth the efforts? A
case report. Microsurgery.;31(3):246-250. http://doi.org/10.1002/micr.20872
[22].
Ferreira,
V., Matos, A., Rego, D., et al., 2017, Percutaneous Treatment Pseudo-Aneurism
of the Hand in Hemophilic Patient. Rev Port Cir Cardiotorac Vasc.;24(3-4):178.
[23].
Cromheecke,
M., van Straalen, A. M., Damen, A., 1997, Traumatic aneurysm of a common
digital artery. J Hand Surg Br.;22(3):416-418. http://doi:10.1016/s0266-7681(97)80417-2

