A Hidden Lake on a Mountain Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising within Verruca Vulgaris in an Uncommon Region
Abstract:
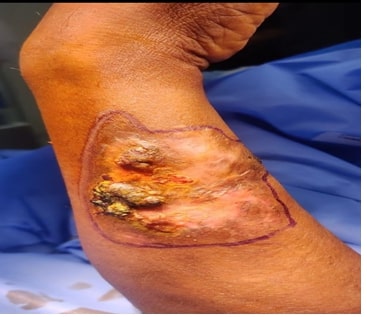
Verruca vulgaris or common warts are benign epidermal growths caused by the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) often found on hands and legs. These lesions are self-limiting varying in number and size and can undergo malignant transformation into SCC. Basal cell carcinoma, the most common type of skin malignancy originates from the basal layer of skin typically in sunlight-exposed areas. And is diagnosed by doing an Edge wedge biopsy and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) tests. Here we present a case report of Basal Cell Carcinoma within a lesion of Verruca vulgaris over the dorsal aspect of the forearm which is an extremely rare presentation.References:
[1]. Grayson, W., 2012, Infectious Diseases of the Skin. In E.
Calonje, T., Brenn, A., Lazar, & P., Mckee (Eds.), Mckee’s Skin
Pathology with Clinical Correlations (4th ed., pp. 760–895). Elsevier.
[2]. Cardoso, J. C., & Calonje, E., 2011, Cutaneous
Manifestations of Human Papillomaviruses: A Review. Acta Dermatovenerologica
Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica, 20(3), 145–154.
[3]. Daugherty, M., & Byler, T., 2018, Genital Wart and
Human Papillomavirus Prevalence in Men in the United States from Penile Swabs:
Results from National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Sexually
Transmitted Diseases, 45(6), 412–416.
[4]. Noel, J. C., Detremmerie, O., Peny, M. O., et al. 1994,
Transformation of Common Warts into Squamous Cell Carcinoma on Sun-Exposed
Areas in an Immunosuppressed Patient. Dermatology, 189(3), 308–311.
[5]. Goette, D. K., 1980, Carcinoma in Situ in Verruca
Vulgaris. International Journal of Dermatology, 19(2), 98–101.
[6]. Ergün, S. S., Su, O., & Büyükbabaný, N., 2004, Giant Verruca
Vulgaris. Dermatologic Surgery, 30(3), 459–462.
[7]. Lai, K. K. H., Chan, E., & Ko, S. C., 2020, Combination
of Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising from a Giant
Verruca Vulgaris Involving the Eyelid. American Journal of Ophthalmology
Case Reports, 21, 100858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajoc.2020.100858
[8]. Sterling, J. C., Handfield-Jones, S., & Hudson, P. M.,
2001, Guidelines for the Management of Cutaneous Warts. British Journal of
Dermatology, 144, 4–11.
[9]. Lipke, M. M., 2006, An Armamentarium of Wart Treatments. Clinical
Medicine & Research, 4(4), 273-293. https://doi.org/10.3121/cmr.4.4.273
[10]. Niculet, E., Craescu, M., Rebegea, L., Bobeica, C.,
Nastase, F., Lupasteanu, G., Stan, D. J., Chioncel, V., Anghel, L., Lungu, M.,
& Tatu, A. L., 2022, Basal Cell Carcinoma: Comprehensive Clinical and Histopathological
Aspects, Novel Imaging Tools and Therapeutic Approaches (Review). Experimental
and Therapeutic Medicine, 23(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10982
[11]. Cohen P. R., 2021, Verruca Vulgaris Occurring on a
Tattoo: Case Report and Review of Tattoo-Associated Human Papillomavirus
Infections. Cureus, 13(8), e17575. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.17575
[12]. Chatterjee, K., Roy, A., Ghosh, R., Barua, J. K., Halder,
S., & Banerjee, G., 2017, The Bumpy Face of Che Guevara: An Interesting
Case. Indian journal of dermatology, 62(6), 675. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijd.IJD_1_17
[13]. Paul, H., Akhtar, N., Zakaria, A. S. M., & Biswas, S.
K., 2017, Generalized Verruca Vulgaris: A Case Report. 6, 29-32.
[14]. Pereira, R. de S., & Monteiro, N. M., 2022,
Successful Treatment of Recalcitrant Non-genital Warts (Verruca vulgaris) with
a Topical Solution Containing Two Antivirals and a Low Concentration of
Salicylic Acid. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International, 34(49B),
1–10. https://doi.org/10.9734/jpri/2022/v34i49B36426
[15]. Aldabagh, B., Angeles, J. G., Cardones, A. R., &
Arron, S. T., 2013, Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Human Papillomavirus:
Is there an Association? *Dermatologic Surgery*, 39(1), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2012.02558.x
[16]. Zaesim, A., Jackson, A. C., Lee, S. W., & Price, S. A.,
2018, Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising within Verruca Vulgaris on the Nipple. Case
Reports in Dermatological Medicine, 2018, 1984593. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1984593
[17]. Kopelson, P. L., Nguyen, Q.
H., & Moy, R. L., 1994, Verruca Vulgaris and Radiation Exposure are
Associated with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Finger. The Journal of
Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology, 20(1), 38-41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1994.tb03747.x
[18]. Ramakrishna, A., Donoghue,
A. O., Mamatha, G. S., & Anuradha, M., 2014, Mucocutaneous Verruca
Vulgaris: A Rare Presentation in an Immunocompetent Patient. Journal of Otology
& Rhinology, 2015.
[19]. Al-Eitan, L. N., Alghamdi,
M. A., Tarkhan, A. H., & Al-Qarqaz, F. A., 2020, Genome-Wide Identification
of Methylated CpG Sites in Nongenital Cutaneous Warts. BMC Medical Genomics,
13(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-020-00751-y
[20]. Zhu, P., Qi, R.-Q., Yang,
Y., Huo, W., Zhang, Y., He, L., Wang, G., Xu, J., Zhang, F., Yang, R., Tu, P.,
Ma, L., Liu, Q., Li, Y., Gu, H., & Cheng, B., 2022, Clinical Guideline for
the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cutaneous Warts. Journal of Evidence-Based
Medicine, 15(3), 12494. https://doi.org/10.1111/jebm.12494

