Prevalence of Antepartum Hemorrhage in Two Referral Hospitals in Douala-Cameroon
Abstract:
A few years after the implementation
of policies to combat maternal mortality, antepartum hemorrhage, which is one of
the main causes, is not systematically documented to the point where we are left
to wonder what it is prevalence in the major cities of Cameroon. This study was
conducted in the Gynecological and Obstetric units of the Laquintinie hospital and
the General hospital of the city of Douala, from May 01, 2020, to April 30, 2022,
has been to determine the prevalence of antepartum hemorrhage in Douala. It included
166 women who had had antepartum hemorrhage. The data collected with an indirect
self-administered questionnaire was processed by SPSS 23. Following this treatment,
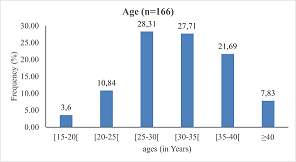
participants had an average age of 31.28 ± 6.33 years. The prevalence of antepartum
hemorrhage in the two hospitals was 3.47% and of 166 cases, 51.80% had placenta
abruption.
References:
[1] Amitava R.S.,
Saikat S.R., Biswa J. N., Gaurab M., Jayanta M., 2010, Management of obstetric haemorrhage.
M. E. J. Anaesth., 20 (4), 499-508.
[2] Lamina M.,
A., Oladapo O.T., 2011, Maternal and Fetal Outcome of Obstetric Emergencies in a
Tertiary Health Institution in SouthWestern Nigeria. Gynecology Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Article ID 160932, 4 doi:10.5402/2011/160932.
[3] Hamadameen,A.I.,
2018, The maternal
and perinatal outcome in antepartum hemorrhage: A cross-sectional study, Zanco J. Med. Sci., 22(2), 155-163,
https://doi.org/10.15218/zjms.2018.021.
[4] Arora R., Devi
U., Majumdar K., 2001, Perinatal morbidity and mortality in antepartum haemorrhage,
J Obstet Gynae India., 51(3):102-104.
[5] Singhal S,
N., Nanda S., 2007, Maternal and perinatal outcome in antepartum hemorrhage : à
study at a tertiary care referral institute. Int J Gynecol Obstet, 9(2). Available
from : https://print.ispub.com/api/0/ispub-article/3465.
[6] Kainer F.,
Hasbargen U., 2008, Emergencies associated with pregnancy and delivery : Peripartum
hemorrhage. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 105 :629‑638.
[7] Lakshmipriya
K., Vijayalakshmi V., Padmanaban S., 2019, A study of maternal and fetal outcome
in Antepartum haemorrhage, Int J Gynecol Obstet, 3(1) :96–99. doi: 10.33545/gynae.2019.v3.i1b.19.
[8] Bhide A, Thilaganathan
B., 2004, Recent advances in the management of placenta previa. Curr Opin Obstet
Gynecol., 16(6):447-451.
[9] Mishra R.,
2014, Ian Donald’s Practical Obstetric Problems. Seventh edition. LWW, 315-328.
[10] Wekere F.,
Chikaike C., Kua P., L., Akani A., B., and Adetomi B., 2021, Prevalence, maternal
and perinatal sequelae of antepartum haemorrhage in a tertiary hospital in southsouth,
Nigeria, International Journal of Clinical Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 5(5), 206-210.
[11] Bener A., Saleh N.M., Yousafzai M.T., 2012, Prevalence
and associated risk factors of ante-partum hemorrhage among Arab women in an economically
fast growing society Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice 15(2), doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.97315,
www.njcponline.com.
[12] Wasnik S. K.,
Naiknaware S. V., 2015, Antepartum haemorrhage: causes and its effects on mother
and child: an evaluation. Obstetrics & Gynecology International Journal, 3(1):00072.
[13] Sharmila G,
Prasanna, 2016, Maternal and perinatal outcome in antepartum hemorrhage. Int Arch
Integr Med, 3(9):148–160.
[14] Onebunne C.
A. C., Christopher O. A., 2019, Prevalence and pregnancy outcomes in patients with
antepartum haemorrhage in a tertiary hospital in Ibadan, Nigeria. International
Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecologywww.ijrcog.org
pISSN 2320-1770 | eISSN 2320-1789; doi:, http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20193017.
[15] Tyagi P., Nidhi
Y., Parul S., Uma G., 2016, Study of antepartum haemorrhage and its maternal and
perinatal outcome ; International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics
and Gynecology, Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol, 5(11), 3972-3977 www.ijrcog.org
pISSN 2320-1770 | eISSN 2320-1789, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20163873.
[16] Adekanle A.,
Adeyemi A., Fadero F., 2011, Antepartum haemorrhage in LAUTECH Teaching Hospital,
South‑Western Nigeria. J Med Sci, 2, 1243‑1247.
[17] Samal S. K.,
Setu R., Reddi R., Seetesh G., 2017, Maternal and perinatal outcomes in cases of
antepartum haemorrhage: a 3-year observational study in a tertiary care hospital;
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology,
6(3):1025-1029; www.ijrcog.org, pISSN 2320-1770 | eISSN 2320-178.
[18] Radhika M.
G., Rajaratnam A., Ayshath S., 2020, Maternal outcome in antepartum Haemorrhage:
A study at a tertiary care Centre International Journal of Clinical Obstetrics and
Gynaecology, 4(5), 05-08.
[19] Kulkarni A.R.,
Shirsath S., 2021, Study of antepartum hemorrhage and its maternal and perinatal
outcome at a tertiary care hospital international Journal of Reproduction, Contraception,
Obstetrics and Gynecology, Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol, 10(6), 2210-2214
www.ijrcog.org pISSN2320-1770 | eISSN2320-1789.
[20] Lankoande M., Bonkoungou P., Ouandaogo S., 2017, Incidence
and outcome of severe antepartum hemorrhage at the Teaching Hospital Yalgado Ouédraogo
in Burkina Faso, BMC Emergency Medicine 17(17). doi 10.1186/s12873-017-0128-3.
[21] Rocha F. E.A.,
Costa M.L., Cecatti J. G., Parpinelli M. A, Haddad S. M., Sousa M. H., Melo E. F.
J. R., Surita F. G., Souza J. P., and the Brazilian network for surveillance of
severe maternal morbidity study group, 2015, Contribution of antepartum and intrapartum
hemorrhage to the burden of maternal near miss and death in a national surveillance
study. Acta Obstet Gynecologica Scandinavica; 94, 50–58.
[22] Langer J., Berger C., Magnin G., 1985, Diagnostic et conduite à tenir devant une grossesse au 3ème trimestre. Obstétrique pour le praticien. Edit SIMEP, 595.
[23] Yadav M. C.,
Mehta K., Choudhary V. A., 2019, A study of antepartum hemorrhage and its maternal
and perinatal outcome at tertiary care hospital in Western Rajasthan. JMSCR, 7(9):80–85.
[24] Park, K. (2007).
Preventive medicine in obstetrics, paediatrics and geriatrics In : Park, textbook
of preventive and social medicine. 19th edition. Banaras Das Bhanot’jabalpur ,445-447.

