Covid-19 Impacts on Elderly with Disability
Abstract:
Covid 19 pandemic created a high mortality risk
among the elderly population, and it also affected more in the case of elderly with
disabilities and elderly people those who have pre-existing comorbidities. The studies conducted worldwide have ingeminate the high risk for medical aid and
increased cases of
death rates in the national level in various countries
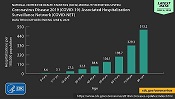
that are dealing with Covid 19 pandemic. One of the shocking news is that 86% of
all death among the elderly population have been reported in two countries, namely Colombia and Chile. In the case of Peru,
70 percent of the death which was reported due to Covid 19 was among elderly people.
In
this study, the author highlights the impacts of Covid
19 among the elderly with a disability, especially concentrating on their mental
health aspects. The world is made up of work pressure, stressful life situations,
and family responsibilities creating difficulties in taking care of elderly people
with disabilities. During
the Covid 19 pandemic, elderly
people with disabilities faced a lot of changes in their life situations, especially
the care and support they received and problems
associated with the satisfaction of basic needs. The elderly
with disability represent a chosen cluster of high-hazard issues
for the growing Covid-19 with a greater chance of impairment.
So, among older people with disabilities, mental health issues
are also higher
than in other age groups. Early prediction and personalized care and management must be provided to the elderly
with disabilities.
References:
[1]. Wang G, Jin X (2020) The progress of
2019 novel coronavirus event in China. J Med Virol. 10.1002/jmv.25705.
[2]. Cohen-Mansfield,
J., Hazan, H., Lerman, Y. and Shalom, V. (2016). Correlates and predictors of loneliness
in older adults: a review of quantitative results informed by qualitative insights.
International Psychogeriatrics, 28, 557–576.
[3]. Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong
Y et al. (2020) Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected
pneumonia. New Engl J Med. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316.
[4]. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and Important
Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary
of a Report of 72 314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
JAMA 2020.
[5]. World
Health Organization. coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) situation report—97. Geneva:
World Health Organization; 2020.
[6]. World
Health Organization. Modes of transmission of the virus causing Covid-19: implications
for IPC precaution recommendations. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020. pp.
10–12.
[7]. The
Indian Express. (2020). older person man in coronavirus isolation ward commits suicide
in Ariyalur General Hospital [Online]. Available at: https://www.newindianexpress.com/states/tamil-nadu/2020/apr/10/older
persons-man-in-corona virus-isolation-ward-commits-suicide-in-ariyalur-general-hospital-2128486.html;
last accessed 7 May 2020.
[8]. Palmieri
L, Andrianou X, Barbariol P et al (2020) Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 patients
dying in Italy report based on available data on April 16th, 2020.
[9]. Jin, Z., Du, X., Xu, Y. et al. Structure of M-pro from SARS-CoV-2
and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 582, 289–293 (2020).
[10]. Meo
SA, Alhowikan AM, al‐Khlaiwi T, et al. Novel coronavirus 2019-CoV: prevalence, biological and clinical
characteristics comparison with SARS‐CoV and MERS‐CoV. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 2020; 24(4): 2012‐ 2019.
[11]. Wu
P, Fang Y, Guan Z, et al. The psychological impact of the SARS epidemic on hospital
employees in China: exposure, risk perception, and altruistic acceptance of risk.
Can J Psychiatry. 2009; 54(5): 302‐ 311.
[12]. Flint,
A.J., Bingham, K.S., and Iaboni, A. (2020). Effect of Covid-19 on the mental health
care of older people in Canada. International Psychogeriatrics. DOI: 10.1017/S104161022000070.
[13].
Debanjan Banerjee (2020). The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic
on elderly mental health. Geriatric Psychiatry. DOI: 10.1002/gps.5320.
[14]. Richard Armitage, Laura B Nellums (2020). Covid-19 and the consequences of isolating
the elderly.
Lancet Public Health. 2020 May;5(5): e256. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30061-X.
[15]. Rukuye Aylaz, Ümmühan Aktürk,
Behice Erci, Hatice Öztürk, Hakime Aslan (2012). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012 Nov-Dec;55(3): 548-54. doi:
10.1016/j.archger.2012.03.006.
Epub 2012 Apr 8.
[16]. Agewell Foundation, (2020). Covid 19 pandemic worsened the situation of
elderly in India: Report. Updated: 13 Jun 2020, https://www.livemint.com/news/india/covid-19-pandemic-worsened-situation-of-elderly-in-india-report-11592058368573.html.
[17]. Flint,
A.J., Bingham, K.S., and Iaboni, A. (2020). Effect of Covid-19 on the mental health
care of older people in Canada. International Psychogeriatrics. DOI: 10.1017/S104161022000070
[18]. Hindustan
Times. (2020). Covid fears: older person couple ends life in Amritsar [Online].
Available at: https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/covid-fear-older persons-couple-ends-life-in-amritsar/story-6jdldsvs4NIlvpPRo71HbJ.html;
last accessed 5 May 2020.
[19]. The
Tribune. (2020). Anxiety over Covid-19 leads to Phagwara woman’s suicide [Online].
https://www.tribuneindia.com/news/punjab/anxiety-over-Covid-19-leads-to-phagwara-womans-suicide-66466;
last accessed 7 May 2020.
[20]. Masters
PS. The molecular biology of corona viruses. Adv Virus Res. 2006; 66: 193–292.
[21]. Kang
S, Peng W, Zhu Y, et al. Recent progress in understanding 2019 novel coronavirus
(SARS-CoV-2) associated with human respiratory disease: detection, mechanisms, and
treatment. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(5):105950. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105950.
[22]. Gorbalenya
AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, et al. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related
coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat Microbiol.
2020; 5:536–544.
[23]. Xu
Y, Li X, Zhu B, et al. Characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential
evidence for persistent fecal viral shedding. Nat Med. 2020; 26: 502–505.
[24]. Hindson
J. Covid-19: fecal-oral transmission? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;
17: 259.
[25]. Nishiura H, Kobayashi T, Suzuki A, et al. Estimation of the asymptomatic ratio of novel coronavirus infections (Covid-19).
[26]. Libertini G, Corbi G, Cellurale M, et al. Age-related dysfunctions: evidence and relationship with some risk factors and protective drugs. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019; 84:1442–1450.
[27]. Lionakis N, Mendrinos D, Sanidas E, et al. Hypertension in the older persons. World J Cardiol. 2012; 4: 135–147.
[28]. Suastika
K, Dwipayana P, Ratna Saraswati IM, et al. Relationship between age and metabolic
disorders in the population of Bali. J Clin Gerontol. 2011; 2: 47–52.
[29]. Moher
D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6: e1000097.

