References:
1. Ahire, S.L., & Golhar, D.Y.
(2001). Quality management in large versus small firms. Journal of Small
Business Management, 27, 1–13.
2. Ahire, L.S., Golhar, D.Y., &
Waller, M.A. (1996). Development and validation of TQM implementation
constructs. Decision Sciences, 27, 23–56.
3. Ahire, S.L., Landeros, R., &
Golhar, D.Y. (1995). Total quality management: A literature review and an
agenda for future research. Production and Operations Management, 4(3),
277–306.
4. Ahmed, P.K. (1998). Culture and
climate for innovation. European Journal of InnovationManagement, 1(1), 30–43.
5. Anderson, J.C., & Gerbing, D.W.
(1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended
two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103, 411–423.
6. Anderson, J.C., Rungtusanatham, M.,
& Schroeder, R.G. (1994). A theory of quality management underlying the
Deming management method. Academy of Management Review, 19(3),472–509.
7. Atuahene-Gima, K. (1996). Market
orientation and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 35(2),93–103.
8. Badri, M.A., Davis, D., &
Davis, D. (1995). A study of measuring the critical factors of quality
management. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management,
2(2), 36–53.
9. Baldwin, J.R., & Johnson, J.
(1996). Business strategies in more and less-innovative firms in
Canada.Research Policy, 25(5), 785–804.
10. Beaumont, N.B., & Sohal, A.S.
(1999). Quality management in Australian service industries.
11. Benchmarking: An International
Journal, 6(2), 107–124.
12. Beaumont, N.B., Sohal, A.S., &
Terziovski, M. (1997). Comparing quality management practices in the Australian
service and manufacturing industries. International Journal of Quality
&Reliability Management, 14(8), 814–833.
13. Black, A.S., & Porter, L.J.
(1996). Identification of the critical factors of TQM. Decision Sciences,27(1),
1–21.
14. Carr, A.S., Leong, G.K., &
Sheu, C. (2000). A study of purchasing practices in Taiwan.
InternationalJournal of Operations & Production Management, 20(12),
1427–1445.
15. Choong, Y.L. (2004). Perception and
development of total quality management in small manufacturers:An exploratory
study in China. Journal of Small Business Management, 42(1),102–115.
16. Crosby, P.B. (1979). Quality is
free. New York: McGraw-Hill
.
17. Crosby, P.B. (1996). Quality is
still free: Making quality certain in uncertain times. New York:McGraw-Hill.
18. Das, A., Paul, H., Swiersek, F.W.,
& Laosirihongthong, T. (2006). A measurement instrument forTQM
implementation in the Thai manufacturing industry. International Journal of
Innovation and Technology Management, 3(4), 1–17.
19. Dean, J.W., & Bowen, D.E.
(1994). Management theory and total quality: Improving research and practice
through theory development. Academy of Management Review, 19(3), 392–418.
20. Dean, J., & Evans, J. (1994).
Total quality management, organization and strategy. St Paul, MN:West
Publishing.948
21. D.T. Hoang et al.Deming, W.E.
(1982). Quality, productivity and competitive position. Cambridge, MA: MIT
Press,Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Center for Advanced Engineering
Study.
22. Deming, W.E. (1986). Out of the
crisis. Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology,Center for
Advanced Engineering Study.
23. Dow, D., Swanson, D., & Ford,
S. (1999). Exploding the myth: Do all quality management practicescontribute to
superior quality performance? Production and Operations Management, 8(1),1–27.
24. Evans, J., & Lindsay, W.
(1993). The management and control of quality (2nd ed.). St Paul, MN:West
Publishing.
25. Feigenbaum, A.V. (1951). Quality
control: Principles, practice, and administration. New York:McGraw-Hill.
26. Feigenbaum, A.V. (1983). Quality
control (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
27. Feigenbaum, A.V. (1991). Total
quality control, 40th anniversary edition (3 rev ed.). New York:McGraw-Hill.
28. Feng, J., Prajogo, D.I., Tan, K.C.,
& Sohal, A.S. (2006). The impact of TQM practices on performance:A
comparative study between Australian and Singaporean organizations. European Journal
of Innovation Management, 9(3), 269–278.
29. Flynn,B.B., Schroeder, R.G., &
Sakakibara, S. (1994).A framework for quality management research and an
associated measurement instrument. Journal of Operational Management,11,
339–366.
30. Gagnon, T., & Toulouse, J.(1996).
The behaviour of business managers when adopting new technologies.
Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 52, 59–74.
31. GAO Study (1991). Report to the
House of Representatives on Management Practices, US Companies Improve
Performance through Quality Efforts. United States General Accounting Office,
Washington, DC.
32. Garvin, D.A. (1988). Managing
quality: The strategic and competitive edge. New York: The Free Press.
33. Germain, R. (1996). The role of
context and structure in radical and incremental logistics innovation adoption.
Journal of Business Research, 35, 117–127.
34. Grant, R.M., Shani, R., &
Krishnan, R. (1994). TQM’s challenge to management theory and practice.Sloan
Management Review, 35(2), 25–35.
35. Haar, J.M., & Spell, C.S.
(2008). Predicting total quality management adoption in New Zealand: The
moderating effect of organizational size. Journal of Enterprise Information
Management,21(2), 162–178.
36. Hair, J.F., Anderson, R.E., Tatham,
R.L., & Black, W.C. (1998). Multivariate data analysis. Upper Saddle River,
NJ: Prentice-Hall International Inc.
37. Hoang, D.T., Igel, B., &
Laosirihongthong, T. (2006). The impact of total quality management on
innovation: Findings from a developing country. International Journal of
Quality &Reliability Management, 23(9), 1092–1117.
38. Hui, M.K., Au, K., & Fock, H.
(2004). Empowerment effects across cultures.Journal of International Business
Studies, 35(1), 46–60.
39. Hung, B.N. (2003). Assesement the
effect of ISO certificate on performance of companies in
40. Hochiminh City. Ho Chi Minh City,
Vietnam: Department of Science, Technology, and Environment, HCMC.
41. Ishikawa, K. (1985). What is total
quality control? Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
42. Joseph, I.N., Rajendran, C., &
Kamalanabhan, T.J. (1999). An instrument for measuring total quality management
implementation in manufacturing-based business units in India.Internal Journal
of Production Research, 37, 2201–2215.
43. Juran, J.M. (1974). Quality control
handbook (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
44. Juran, J.M. (1988). Juran on
planning for quality. New York: Free Press.
45. Juran, J.M. (1989). Juran on
leadership for quality: an executive handbook. New York: Free Press.
46. Juran, J.M. (1992). Juran on
quality by design: The new steps for planning quality into goods and services.
New York: Free Press.
47. Juran, J.M. (1995). A history of
managing for quality: The evolution, trends and future direction of managing
for quality. Milwaukee, WI: ASQC Quality Press.
48. Kim, W.C., & Marbougne, R.
(1999). Strategy, value innovation, and the knowledge economy.Sloan Management
Review, (Spring), 41 –54.Total Quality Management 949Kline, R.B. (1998).
Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York: The Guilford
Press.
49. Kruger,V.](1996).How can a company
achieve improved levels of quality performance: Technology versus employees?
The TQM Magazine, 8(3), 11–20.
50. Kruger, V. (1998). Total quality
management and its humanistic orientation towards organisationalanalysis. The
TQM Magazine, 10(4), 293–301.
51. Kruger, V. (2001). Main schools of
TQM: ‘the big five’. The TQM Magazine, 13(3), 146–155.
52. Laosirihongthong, T, Paul, H.,
& Speece, M.W. (2003). Evaluation of new manufacturing technology
implementation: And empirical study in the Thai automotive
industry.Technovation, 23, 321 –331.
53. Loan, N.T.Q. (2004). Assesment of
the quality management system of ISO companies. Economic Development Review,
University of Economics, Ho Chi Minh City, No. 8–9.
54. McAdam, R., Armstrong, G., &
Kelly, B. (1998). Investigation of the relationship between totalquality and
innovation: A research study involving small organizations. European Journal of
Innovation Management, 1(3), 139–147.
55. Millar, R.M.G. (1987). In foreword
to J. Cullen & J. Hollingham. Implementing total quality.Bedford: IFS
Publications. Ministry of Planning and Investment. (1999). Research report:
Improving macroeconomic policy and reforming administrative procedures to
promote development of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam.
56. Motwani, J. (2001). Critical
factors and performance measures of TQM. The TQM Magazine, 13(4),292–300.
57. Noronha, C. (2002). Chinese
cultural values and total quality climate. Managing Service Quality,12(4),
210–223.
58. Nunnally, J., & Burnstein, I.H.
(1994). Pschychometric theory (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
59. Pinho, J.C. (2008). TQM and
performance in small medium enterprises: The mediating effect of
customerorientation and innovation. International Journal of Quality &
Reliability Management,25(3), 256–275.
60. Powell, T.C. (1995). Total quality
management as competitive advantage: A review and empiricalstudy. Strategic
Management Journal, 16, 15–37.
61. Power, D.J., Amrik, S.S., &
Rahman, S. (2001). Critical success factors in agile supply chain
management.International Journal of Physical Distribution and Logistics
Management, 31(4),247–265.
62. Prajogo, D.I. (2005). The
comparative analysis of TQM practices and quality performance between
manufacturing and service firms. International Journal of Service Industry Management,16(3),
217–228.
63. Prajogo, D.I., & Sohal, A.S.
(2003a). The multidimensionality of TQM practices in determining quality and
innovation performance – an empirical examination. Technovation, 24, 443–453.
64. Prajogo, D.I., & Sohal, A.S.
(2003b). The relationship between TQM practices, quality performance,and
innovation performance: An empirical examination. International Journal of
Quality & Reliability Management, 20(8), 901–918.
65. Prajogo, D.I., & Sohal, A.S.
(2006). The integration of TQM and technology /R&D management in
determining quality and innovation performance. The International Journal of
Management Science, Omega, 34, 296–312.
66. Pun, K.F. (2001). Cultural
influences of TQM adoption in Chinese enterprises: An empirical study.Total
Quality Management, 12(3), 323–342.
67. Rahman, S., & Bullock, P.
(2005). Soft TQM, hard TQM, and organisational performance relationship:An
empirical investigation. Omega, 33, 73–83.
68. Reed, R., Lemark, D.J., & Mero,
N.P. (2000). Total quality management and sustainable competitive advantage.
Journal of Quality Management, 5, 5–26.
69. Samson, D., & Terziovski, M.
(1999). The relationship between total quality management practices and
operational performance. Journal of Operations Management, 17, 393–409.
70. Saraph, J.V., Benson, G.P., &
Schroeder, R.G. (1989). An instrument for measuring the criticalfactors of
quality management. Decision Sciences, 20, 810 –829.
71. Sila, I., & Ebrahimpour, M.
(2002). An investigation of the total quality management survey based research
published between 1989 and 2000 – a literature review. International Journal
ofQuality & Reliability Management, 19(7), 902–970.950 D.T. Hoang et al.
72. Silvestro, R. (1998). The
manufacturing TQM and service quality literatures: Synergistic or conflicting
paradigms? International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management,
15(3), 303–328.
73. Singh, P.J., & Smith, A.F.R.
(2004). Relationship between TQM and innovation: An empirical studyJournal of
Manufacturing Technology Management, 15(5), 394–401.
74. Sitkin, S.B., Sutcliffe, K.M.,
& Schroeder, R.G. (1994). Distinguishing control from learning in
totalquality management: A contingency perspective. Academy of Management
Review, 19(3),537–564.
75. Slater, S.F., & Narver, J.C.
(1998). Customer-led and market-led: Let’s not confuse the two.Strategic
Management Journal, 19(10), 1001–1006.
76. Spreitzer, G.M. (1995).
Psychological empowerment in the work place: Dimensions, measurementand validation.
Academy of Management Journal, 38(5), 1442–1465.
77. Steingrad, D.S., & Fitzgibbons,
D.E. (1993). A postmodern deconstruction of total quality managementJournal of
Organization Change Management, 6(5), 27–42.
78. Sureshchandar, G.S.,
Chandrasekharan, R., & Anantharaman, R.N. (2001). A conceptual model
fortotal quality management in service organizations. Total quality management,
12(3),343–363.
79. Swamidass, P.M., & Kotha, S.
(1998). Explaining manufacturing technology use firm size and performance usinga
multidimensional view of technology. Journal of Operation Management,17, 23–37.
80. Terziovski, M., & Samson, D.
(1999). The link between total quality management practice and
81. organizational performance.
International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management,16(3), 226–237.
82. Terziovski, M., & Samson, D.
(2000). The effect of company size on the relationship between TQM strategy and
organizational performance. The TQM Magazine, 12(2), 144–148.
83. Tidd, J., Bessant, J., & Pavitt,
K. (1997). Managing innovation: Integrating technological, market,and
organizational change. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
84. Vuppalapati, K., Ahire, S.L., &
Gupta, T.(1995). JIT and TQM: A case for joint implementation.International
Journal of Operations & Production Management, 15(5), 84–94.
85. Watson,J.G., & Korukonda, A.R.
(1995). The TQM jungle: A dialectical analysis.InternationalJournal of Quality
& Reliability Management, 12(9), 100–109.
86. Wind, J., & Mahajan, V. (1997).
Issues and opportunities in new product development: An introduction to the
special issue. Journal of Marketing Research, 34(1), 1–12.
87. Woon, K.C. (2000). TQM
implementation: comparing Singapore’s service and manufacturing
88. leaders. Managing Service Quality,
10(5), 318–331.
89. Yavas, B.F., & Rezayat, F.
(2003). The impact of culture on managerial perceptions of
quality.International Journal of Cross Cultural Management, 3(2), 213–234.
90. Zeithaml,V.A., Parasuraman, A.,
& Berry, L.L. (1990).Delivering quality service: Balancing customer
perceptions and expectations. New York: Free Press.
91. Zeitz, G.,Johannesson, R., &
Ritchie, J.E. Jr. (1997). An employee survey measuring total quality management
practices and culture. Group and Organization Management, 22(4), 414–444.

 Pregnant Women’s Perception of Maternity Care Given in Ladoke Akintola University Teaching Hospital, Osogbo, Osun State, Nigeria West AfricaAuthor: Clementina Obby Ezenwuba
Pregnant Women’s Perception of Maternity Care Given in Ladoke Akintola University Teaching Hospital, Osogbo, Osun State, Nigeria West AfricaAuthor: Clementina Obby Ezenwuba Achieving Healthy Weight in African-American Communities: Research Perspectives and PrioritiesAuthor: Iweriebor Onoiribholo Bridget
Achieving Healthy Weight in African-American Communities: Research Perspectives and PrioritiesAuthor: Iweriebor Onoiribholo Bridget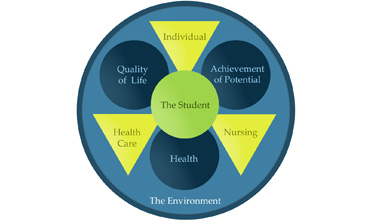 A Holistic Framework for Nursing Time: Implications for Theory, Practice, and ResearchAuthor: Surriya Shahnaz
A Holistic Framework for Nursing Time: Implications for Theory, Practice, and ResearchAuthor: Surriya Shahnaz Legal Awareness and Responsibilities of Nursing Staff in Administration of Patient Care in a Trust HospitalAuthor: Oluwatosin Oluwaseun Olu-Abiodun
Legal Awareness and Responsibilities of Nursing Staff in Administration of Patient Care in a Trust HospitalAuthor: Oluwatosin Oluwaseun Olu-Abiodun Total Quality Management (TQM) Strategy and Organizational Characteristics: Evidence from a Recent WTO MemberAuthor: Rukhsana Kousar
Total Quality Management (TQM) Strategy and Organizational Characteristics: Evidence from a Recent WTO MemberAuthor: Rukhsana Kousar