Fat Embolism Syndrome in Fracture Tibia Treated by Unreamed Interlocking Nail
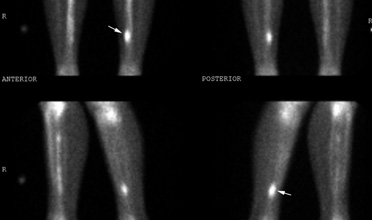
Abstract:
Fat embolism
syndrome (FES) occurs when embolic fat macro globules pass into the small
vessels of the lung and other sites, producing endothelial damage and resulting
respiratory failure (ARDS-like picture), cerebral dysfunction and a petechial
rash. The incidence of fat emboslism in all kinds of fractures is about 16% but
sometimes it is as high as 50% to 62%. The fat embolism is common in fatty and
bed ridden patients and in whom reamed interlocking is performed under
tourniquet and surgery is to be delayed. But in the case discussed by us
unreamed interlocking was performed without tourniquet and the operative procedure
was done within 4 hours after trauma and the pre-operative investigation were
within normal limits. Patient was lean and thin. The present case report is
discussed to convey the message that even when surgeon takes every precaution
for prevention of fat embolism, it can occur in any case.
References:
[1.] Tzun, Tsai, Chin-Jung, Hsu, Ying-Hao, Chen, Yi-Chin,
Fong, Horng-Chaung, HSU, et al (2010). Fat Embolism syndrome in long bone
fracture – clinical experience in a terliary referral center in Tawian. Journal
of the Chines Medical Association, 73 (8), 407-410.
[2.] James ,C., Glazer, & Danie,l K., Orian. Fat
embolism syndrome in a surgical Patient. JABFP, vol 14, No. 4.
[3.] Stein, P.D., Yaekoub, A.Y, Matta, F., et al (2008).
Embolism syndrome. Am J Med Sci, 336(6), 472-477.
[4.] Taviloglu, K., Yanar, H. (2007). Fat embolism
syndrome. Surg Today, 37(1), 5-8.
[5.] Tumerdem, B., Onel, D., Topalan, M., Korpinar, S.,
Aktas, S (2008) Fat embolism syndrome after lower extremity replantation
associated with libia fracture : case report. Ulus Travma. Acil Cerrahi Derg,
14(1), 73-75.

