Enhancing Non-profit Efficiency and Impact Through Data-Driven Strategies: Addressing Challenges and Leveraging Emerging Technologies - A Literature Review
Abstract:
Evidence
based strategy formulation using data has become a method to enhance
organizations' efficiency and decision-making processes in a more accountable
manner. This article examines how adopting data-driven approaches affects
strategies, resource allocation, and the cultivation of trust with
stakeholders. After analysing secondary data sources, this research focuses on
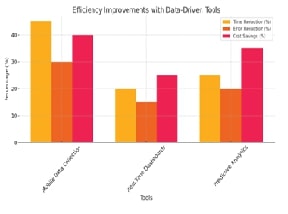
key tools such as mobile data collection, predictive analytics, and dashboards
that significantly improve efficiency by reducing time consumption and errors
by approximately 45% and 30%, respectively. Effective data governance practices
improve transparency and inspire donors' trust within organizations, along with
advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). Blockchain is expected to drive
enhancements in this regard. Emerging technologies like blockchain are expected
to enhance transparency and donor trust, further driving data governance
improvements. However, challenges such as resources, scattered data, and
ethical concerns continue to pose hurdles for smaller nonprofit organizations.
Suggestions encompass skill development initiatives, cost-effective technology
solutions, and collaborative alliances. The research reinforces the importance
of embracing data-centric approaches for lasting outcomes and offers guidance
for professionals and policymakers alike. It would be beneficial to explore how
these methods could contribute to sustainability and their practical use in
industries aiming to bring about long-term positive impacts.
References:
[1].
Barney, J., 1991. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Journal
of Management, 17(1), 99–120. https://doi.org/10.1177/014920639101700107
[2].
Bertalanffy, L., von., 1968. General system theory: Foundations, development,
applications. George Braziller.
[3].
Burns, T., & Stalker, G. M., 1961. The management of innovation. Tavistock.
[4].
Davenport, T. H., & Harris, J.
G., 2007.
Competing on analytics: The new science of winning. Harvard Business Review
Press.
[5].
Digital Impact Alliance., 2020. Accelerating real-time data collection in nonprofits.
Retrieved from https://www.digitalimpactalliance.org
[6].
Few, S., 2012. Show me the numbers:
Designing tables and graphs to enlighten. Analytics Press.
[7].
Harvard Social Impact Report. 2022.
The rise of predictive analytics in nonprofit decision-making. Retrieved from https://www.harvardsocialimpact.org
[8].
International Federation of Red
Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)., 2022.
Enhancing disaster response through predictive analytics. Retrieved from https://www.ifrc.org
[9].
Kobo Toolbox. n.d. Real-time data
collection for nonprofits. Retrieved from https://www.kobotoolbox.org
[10].
Kotler, P., & Lee, N., 2009. Up and out of poverty: The social marketing solution.
Pearson Education.
[11].
Nonprofit Tech for Good., 2023. Global trends in data-driven nonprofit strategies.
Retrieved from https://www.nonprofittechforgood.com
[12].
PATH. n.d. Mobile impact data
collection for rural health initiatives. Retrieved from https://www.path.org
[13].
Provost, F., & Fawcett, T., 2013. Data science for business. O'Reilly Media.
[14].
Saunders, M., Lewis, P., &
Thornhill, A.,
2019.
Research methods for business students (8th ed.). Pearson Education.
[15].
Tapscott, D., & Tapscott, A., 2016. Blockchain revolution: How the technology behind
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is changing the world. Penguin.
[16].
United Nations. 2015. Transforming
our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development. Retrieved from https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda
[17].
Weiss, C. H., 1995. Nothing as practical as good theory: Exploring
theory-based evaluation for comprehensive community initiatives. In New
approaches to evaluating community initiatives: Concepts, methods, and contexts
(pp. 65–92). Aspen Institute.
[18].
Wilson, H. J., & Daugherty, P.
R. 2018. Collaborative intelligence: Humans and AI are joining forces. Harvard
Business Review.
[19].
World Bank Report. 2021. Addressing
connectivity challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa. Retrieved from https://www.worldbank.org
[20].
World Health Organization (WHO)
2021. Leveraging health data for effective nonprofit interventions. Retrieved
from https://www.who.int
[21].
Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
n.d. Our approach to data-driven decision making. Retrieved from https://www.gatesfoundation.org
[22].
American Red Cross. 2020.
Data-driven disaster response. Retrieved from https://www.redcross.org
[23].
Charity Water. n.d. Tracking our
projects with transparency. Retrieved from https://www.charitywater.org
[24].
John Snow, Inc. (JSI). (n.d.).
Digital tools for real-time data collection: Improving health outcomes through
efficient data management. Retrieved from https://publications.jsi.com/JSIInternet/Inc/Common/_download_pub.cfm?id=13532&lid=3
[25].
United Nations Development Programme
(UNDP) n.d. SURGE Data Hub: Supporting digital assessments for crisis response.
Retrieved from https://data.undp.org/insights/surge-data-hub
[26].
African Development Bank (AfDB).
2020. Application of SurveyCTO mobile data collection tools for household
surveys
[27]. MIT Sloan Management Review. n.d. Improve key performance indicators with AI.

